The Power of Gesture Control Devices: Revolutionising

In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, gesture control devices have emerged as game-changers, revolutionising the way we interact with various technologies. From gaming and smart home automation to healthcare and robotics, these devices offer a seamless and intuitive user experience. In this article, we will delve into the world of gesture control devices, exploring their key features, applications, challenges, and future trends. Get ready to embark on an exciting journey of gesture-based innovation.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Gesture Control Technology:
Gesture control technology harnesses the power of human gestures to facilitate interaction with devices. By analysing hand movements, body language, and facial expressions, these devices translate our physical cues into meaningful commands. This groundbreaking technology has become increasingly prevalent, thanks to advancements in computer vision and machine learning algorithms. Notable examples of gesture control devices include the Microsoft Kinect, Leap Motion, and Myo armband.
Key Features and Benefits of Gesture Control Devices:
Gesture control devices offer a multitude of benefits, enhancing the user experience and revolutionising interaction. By eliminating the need for physical controllers, these devices enable hands-free operation, providing a new level of convenience and freedom. Furthermore, gesture control devices promote accessibility and inclusivity by accommodating users with mobility impairments. With improved precision and control, users can execute commands effortlessly, unlocking new possibilities in gaming, automation, healthcare, and beyond.
key features and functionalities of three popular gesture control devices:
| gesture control devices | Microsoft Kinect | Leap Motion | Myo Armband |
| Device Type | Camera-based | Sensor-based | Wearable |
| Key Technology | Depth sensing camera | Infrared sensors and cameras | Electromyography (EMG) and motion sensors |
| Tracking Range | Up to 6 meters | Up to 1 meter | Arm and hand movements |
| Gesture Recognition | Full-body tracking with skeletal mapping | Hand and finger tracking | Hand and arm movements |
| Hand Gestures | Supports a wide range of hand and body gestures | Recognizes hand and finger movements | Recognizes various hand and arm gestures |
| Application Range | Gaming, entertainment, fitness, healthcare, and more | Virtual reality, gaming, design, robotics, and more | Gaming, virtual reality, prosthetic control, and more |
| Device Compatibility | Xbox consoles, Windows PCs | Windows PCs, Mac, Linux | Windows PCs, Mac, Android, iOS |
| SDK Availability | Provides a comprehensive software development kit (SDK) | Offers a robust SDK with APIs for application development | Provides an SDK with APIs for developers to create apps |
| Accuracy | High | High | Moderate to high |
| User Experience | Immersive and responsive interaction | Precise and fluid hand tracking | Intuitive and natural arm and hand control |
| Limitations | Requires adequate space for full-body tracking | Limited tracking range and sensitivity | May have occasional false positives or missed gestures |
| Cost | Relatively higher cost compared to other devices | Moderately priced | Moderately priced |
Applications of Gesture Control Devices:
Gesture-based gaming: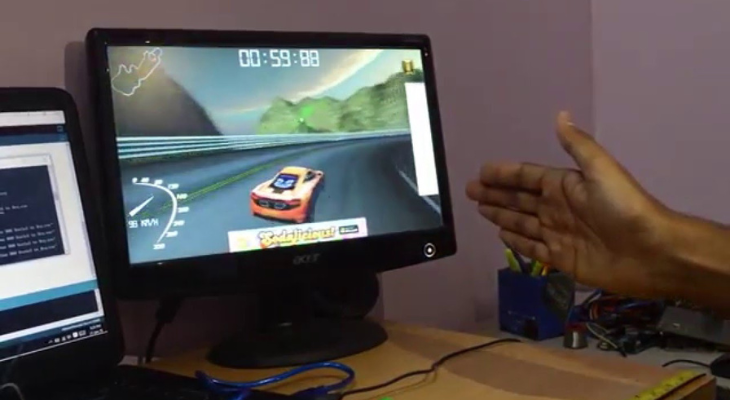
Gesture control devices have transformed the gaming landscape, immersing players in interactive experiences. By intuitively mimicking real-world actions, users can swing swords, throw virtual objects, or steer vehicles, creating a more engaging and immersive gameplay experience.
Gesture-controlled home devices:
With gesture control, managing smart home devices becomes a breeze. Users can effortlessly adjust lighting, control temperature, and operate appliances with simple hand gestures, eliminating the need for physical switches or smartphone apps.
Gesture-controlled medical equipment: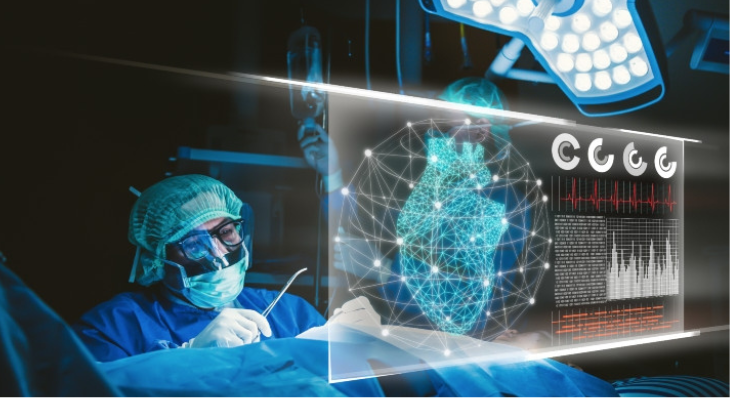
Gesture control devices are revolutionizing healthcare, enhancing medical equipment usability. Surgeons can manipulate images during surgeries, doctors can navigate patient records without physical contact, and patients with limited mobility can control assistive devices using gestures.
Automotive industry gesture-based car controls: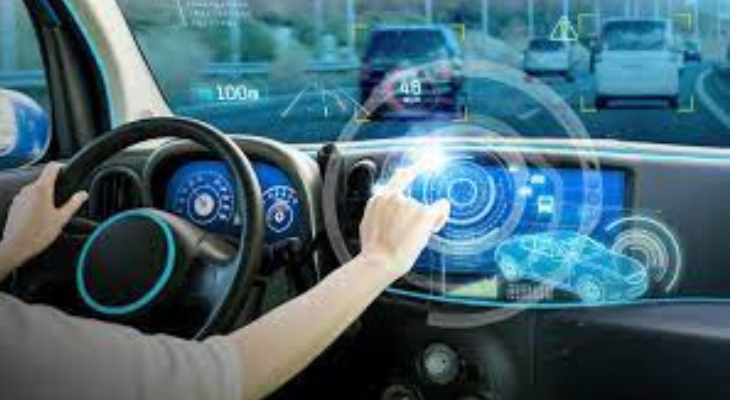
Gesture control is making its way into the automotive industry, enabling drivers to interact with infotainment systems, adjust settings, and answer calls without taking their hands off the steering wheel. This promotes safer driving and reduces distractions.
Gesture-Based Robotics: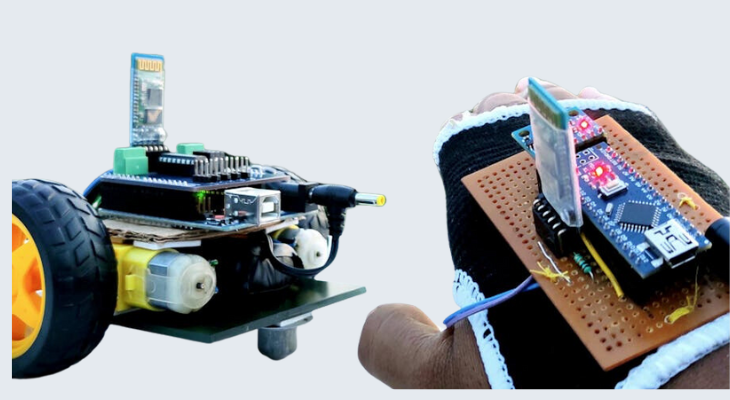
Gesture control devices have opened up new frontiers in robotics. By employing gestures, users can remotely control robots, enabling intuitive and natural interactions. Gesture-based robotics finds applications in industrial automation, exploration, and even personal assistants.
Challenges and Limitations of Gesture Control Devices:
While gesture control devices have immense potential, they also face challenges. Users may experience a learning curve when adapting to new gesture commands. Sensitivity and accuracy issues can arise due to varying environmental factors, impacting device performance. Ongoing research and development aim to overcome these challenges and improve the technology further.
Future Trends and Developments in Gesture Control Technology:
The future of gesture control technology is promising. Integration with artificial intelligence will enable devices to learn and adapt to users’ unique gestures, enhancing accuracy and personalization. Furthermore, gesture control technology will expand into new industries, driving innovation in fields such as education, entertainment, and healthcare. Exciting times lie ahead as gesture control becomes more pervasive in our daily lives.
Steps for Setting Up and Using Gesture Control Devices:
Step 1: Check Device Compatibility and Setup
Ensure that your device is compatible with the gesture control device you intend to use.
Connect the gesture control device to your device using the provided cables or wireless connection methods.
Install any necessary drivers or software required for the gesture control device to function properly.
Step 2: Calibrate the Gesture Control System
Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer to calibrate the gesture control system. Calibration ensures accurate recognition of your gestures.
Typically, this involves positioning yourself within the designated range and performing specific gestures as prompted by the calibration process.
Pay attention to any recommended lighting conditions or other environmental factors mentioned during calibration.
Step 3: Learn and Practice Gesture Commands
Familiarize yourself with the available gesture commands supported by your device. These commands may vary depending on the application or device you are using.
Consult the user manual or online resources provided by the manufacturer to learn the specific gestures and their corresponding functions.
Practice executing the gestures in a clear and deliberate manner to ensure accurate recognition by the device.
Experiment with different hand movements, postures, and speeds to understand the device’s sensitivity and fine-tune your gestures if necessary.
Step 4: Adjust Device Settings and Customization (if available)
Explore the device settings and customization options to tailor the gesture control experience to your preferences.
Adjust sensitivity settings to accommodate your hand size, gestures, or personal comfort.
If the device supports customization, such as assigning specific gestures to certain functions or creating gesture shortcuts, take advantage of these features to streamline your interaction.
Step 5: Practice and Refine Your Gesture Control Skills
Regular practice is key to mastering gesture control. Set aside dedicated time to use the device and practice executing gestures accurately.
Monitor your interactions and observe any patterns or gestures that may require improvement.
Take note of any challenges or areas where the device may have difficulty recognizing your gestures and adjust accordingly.
Step 6: Stay Updated and Explore New Gestures and Applications
- Stay informed about firmware updates, software enhancements, or new gesture control applications released by the manufacturer.
- Continuously explore new gestures and functionalities that may be introduced through updates or third-party applications.
- Engage with online communities, forums, or user groups to learn from others’ experiences and discover innovative ways to maximize your gesture control device’s potential.
Pros and cons of gesture control devices:
| Pros | Cons |
| Enhanced user experience and interaction | Learning curve for new users |
| Hands-free operation | Sensitivity and accuracy issues |
| Accessibility and inclusivity | Environmental factors affecting performance |
| Improved precision and control | Limited gesture recognition capabilities |
| Immersive and intuitive interaction | Potential false positives or missed gestures |
| Wide range of applications and industries | Limited range or field of view for tracking |
| Potential for innovation and future growth | Relatively higher cost compared to traditional input |
Conclusion:
Gesture control devices have revolutionized the way we interact with technology, offering an intuitive and immersive experience. From gaming to healthcare, smart homes to robotics, these devices are shaping the future of human-machine interaction. As research and development continue to push the boundaries of gesture control technology, we can expect even more exciting innovations and applications. Embrace the power of gestures and unlock a new dimension of interaction. The future is at your fingertips.
Steps for Setting Up and Using Gesture Control Devices:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Gesture Control Devices:
What are the primary applications of gesture control devices?
Gesture control devices have a wide range of applications, including gaming, virtual reality, smart home automation, healthcare, robotics, and the automotive industry. They offer intuitive and hands-free interaction, enhancing user experiences across various domains.
Can gesture control devices be customized for specific tasks?
Yes, many gesture control devices offer customization options. Users can often configure gesture commands, sensitivity settings, and assign specific gestures to perform certain functions. This flexibility allows users to tailor the devices to their preferences and specific application requirements.
Are there any privacy concerns related to gesture control technology?
Gesture control technology primarily relies on capturing and interpreting physical gestures and movements. While devices prioritize user privacy, it is essential to be mindful of the data collected and stored by these devices. Users should review privacy policies and settings to understand how their information is handled and take the necessary precautions to protect their privacy.
How reliable and accurate are gesture control devices?
Gesture control devices have significantly improved in reliability and accuracy over the years. However, their performance may be influenced by factors such as environmental conditions, lighting, and user technique. It’s important to familiarize yourself with the device’s limitations and follow proper calibration and usage instructions for optimal performance.
How do gesture control devices impact accessibility for individuals with disabilities?
Gesture control devices have the potential to greatly enhance accessibility for individuals with disabilities. By offering hands-free operation and intuitive interactions, these devices enable users with mobility impairments to access and control various technologies more easily. However, it’s crucial to ensure that gesture control devices are designed with inclusivity in mind and offer alternative input methods for individuals who may have difficulty with gestures.





2 Comments