Blockchain Technology: How It Works and Applications

In this article, we’re going to dive into the fascinating world of blockchain technology, exploring what it is, how it works, its myriad applications, benefits, and challenges. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just curious about this innovative technology, this guide will take you through the fundamentals and leave you with a clear understanding.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Blockchain Technology and How does blockchain work?
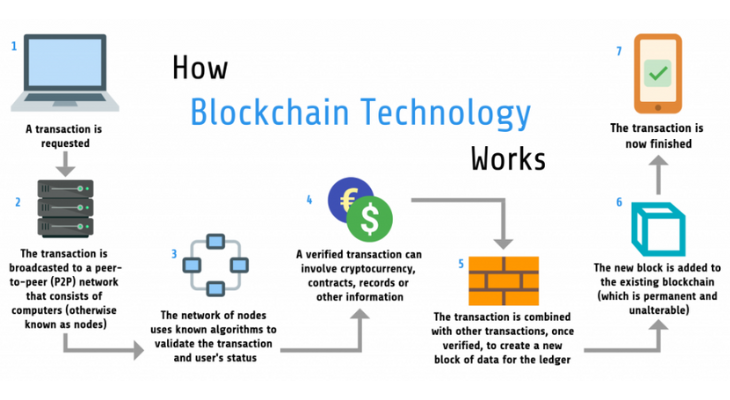
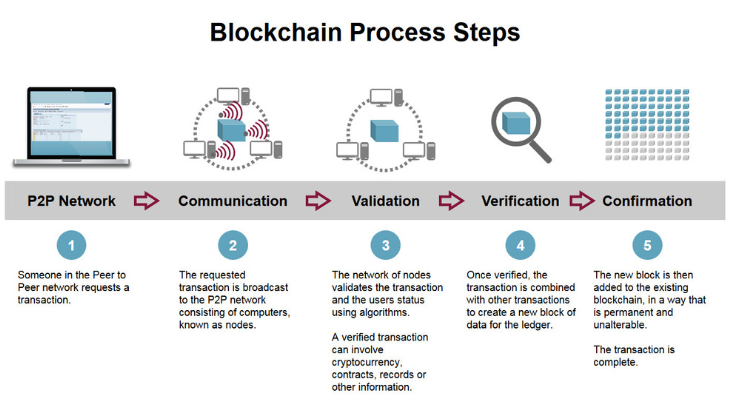
Blockchain technology has been making waves in recent years, but what is it, and how does it function? In a nutshell, it’s a decentralized, distributed ledger system that uses cryptography to secure data and transactions. Each block in the chain contains a group of transactions, and these blocks are linked together, forming a chronological chain.Blockchain Meaning is to put it simply, blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It’s like a shared, secure database that can be accessed by anyone in the network.
Types of blockchain technology
- Public Blockchain
- Private Blockchain
- Consortium Blockchain
- Hybrid Blockchain
- Permissioned Blockchain
- Blockchain as a Service (BaaS)
- Federated Blockchain
- Sidechains
- Smart Contract Platforms
- Sharded Blockchains
- Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)
- Public Blockchain:
- Public blockchains are open to anyone and are permissionless. Anyone can join, participate, and validate transactions on the network.
- Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Binance Smart Chain.
- Use Cases: Open financial systems, decentralized apps (DApps), and cryptocurrencies.
- Private Blockchain:
- Private blockchains are restricted to a select group of participants who are granted permission to access and validate transactions.
- Examples: Hyperledger Fabric, Corda.
- Use Cases: Enterprise solutions, supply chain management, and business consortiums.
- Consortium Blockchain:
- Consortium blockchains are semi-private and are governed by a consortium of organizations or entities rather than a single entity.
- Use Cases: Collaborative industry projects, supply chain networks, and inter-organizational platforms.
- Hybrid Blockchain:
- Public and private blockchain components are combined in hybrid blockchains.
- They offer flexibility in terms of permissioning and data visibility.
- Use Cases: Cross-industry solutions, combining public and private functionalities as needed.
- Permissioned Blockchain:
- Permissioned blockchains require participants to be authorized, making them suitable for enterprise and government use. Access controls are in place.
- Use Cases: Secure data sharing, government records, and enterprise solutions.
- Blockchain as a Service (BaaS):
- BaaS is a cloud-based service that allows users to develop, host, and manage blockchain applications without the complexity of building and maintaining a blockchain infrastructure.
- Examples: Microsoft Azure Blockchain, IBM Blockchain Platform.
- Use Cases: Rapid development and deployment of blockchain applications.
- Federated Blockchain:
- Federated blockchains are a form of consortium blockchain where a group of organizations collaboratively control the network.
- Use Cases: Interoperable supply chain solutions, industry-specific consortiums.
- Sidechains:
- Sidechains are separate blockchains that are linked to a primary blockchain, often referred to as the “mainchain.” They enable off-chain scaling and can have different rules or features.
- Use Cases: Scalability solutions, cross-chain compatibility, and experimentation with new features.
- Smart Contract Platforms:
- These blockchains are designed primarily for creating and executing smart contracts. They offer programmable functionality, enabling automated and self-executing agreements.
- Examples: Ethereum, EOS.
- Use Cases: Decentralized applications, token creation, and automated agreements.
- Sharded Blockchains:
- Sharded blockchains split the network into smaller partitions called shards. Each shard processes its transactions, increasing scalability.
- Use Cases: Scalability solutions for large blockchain networks.
- Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG):
- DAG is an alternative to the traditional blockchain structure. Instead of a linear chain, it uses a graph-like structure where transactions are linked in a non-linear manner.
- Examples: IOTA, Nano.
- Use Cases: IoT (Internet of Things), feeless microtransactions, and instant processing.
Core Concepts of Blockchain
Decentralization: One of the core concepts of blockchain is decentralization. Blockchain runs on a network of computers, as opposed to conventional centralized systems, which are governed by a single authority.This eliminates the need for a central entity and enhances security and transparency.
Distributed Ledger : Every participant in the network has a copy of the ledger. This distributed ledger ensures that all transactions are transparent and can be verified by anyone on the network.
Cryptography :Cryptography is the foundation of blockchain security. It ensures that data is secure and that only authorized individuals can access and modify it.
Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain relies on consensus mechanisms to validate and add transactions to the ledger.These systems make sure that everyone is in agreement with the blockchain’s current status.
Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain technology isn’t limited to cryptocurrencies; its applications are diverse and far-reaching.
Cryptocurrencies :The most famous application of blockchain is in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Peer-to-peer secure transactions are made possible without the use of middlemen like banks.
Supply Chain Management :Blockchain is revolutionizing supply chain management by providing end-to-end visibility. This ensures the authenticity and quality of products throughout the supply chain.
Healthcare: In healthcare, blockchain is used to securely store and share patient records, ensuring data accuracy and patient privacy.
Voting Systems: Blockchain can be used to create transparent and tamper-proof voting systems, reducing fraud and increasing trust in elections.
Real Estate :The real estate industry is benefiting from blockchain’s ability to streamline property transactions and reduce fraud.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
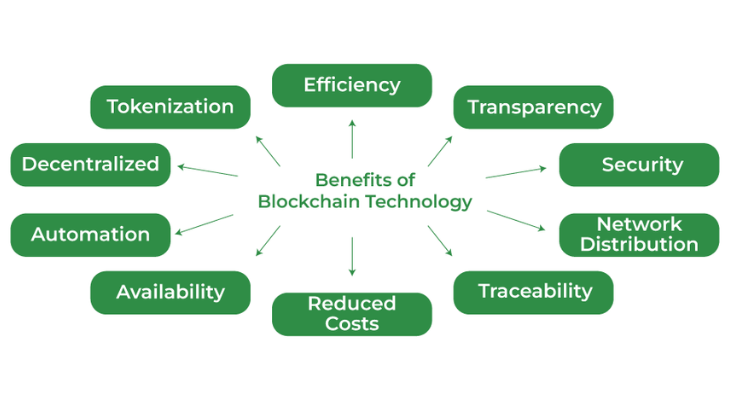
Blockchain technology comes with a host of benefits.
Gratitude :Blockchain is very secure because of its decentralized architecture and usage of cryptography.Once data is added to the chain, it’s nearly impossible to alter or delete.
Transparency: The distributed ledger ensures that all transactions are visible and verifiable, enhancing trust among participants.
Effectiveness :Because blockchain eliminates the need for middlemen, procedures are streamlined and expenses are decreased.
Reduced Fraud :The immutability of the ledger makes it incredibly difficult for fraudulent activities to occur.
Cost Savings :With fewer intermediaries and increased efficiency, blockchain can lead to significant cost savings in various industries.
Challenges and Concerns
While blockchain has immense potential, it also faces some challenges.
Reliability :Scalability becomes an issue as blockchain networks expand. Efforts are ongoing to improve the speed and capacity of these networks.
Regulatory Issues :Blockchain’s decentralized nature has led to regulatory challenges, with governments worldwide working to establish legal frameworks.
Environmental Impact :The energy consumption of some blockchain networks, particularly Bitcoin, has raised concerns about its environmental impact.
Privacy Concerns :Balancing the transparency of blockchain with privacy concerns is an ongoing challenge.
Emerging Trends in Blockchain
Blockchain technology is constantly evolving. Here are some emerging trends:
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) :DeFi platforms are using smart contracts to create decentralized alternatives to traditional financial services.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) :NFTs have taken the art and entertainment world by storm, utilizing blockchain for the creation and trading of unique digital assets.
Cross-Chain Integration :Efforts are underway to connect different blockchain networks, allowing for seamless data transfer and transactions.
Blockchain Interoperability :Blockchain interoperability aims to create a standardized framework for different blockchains to communicate and work together.
Advantages of blockchain technology
Security:
Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it is nearly impossible to alter, ensuring the integrity of data.
Transparency:
All transactions on a blockchain are visible to participants in the network. This transparency fosters trust, as users can independently verify and audit transactions.
Trust:
The transparent and tamper-proof nature of blockchain technology builds trust among participants. Users can have confidence that the data on the blockchain is accurate and reliable.
Efficiency:
Blockchain reduces the need for intermediaries in transactions. This streamlines processes, speeds up settlement times, and reduces costs, making it more efficient than traditional systems.
Reduced Fraud:
The immutability of blockchain records makes it highly resistant to fraud. It’s difficult for malicious actors to manipulate data or conduct fraudulent activities.
Cost Savings:
By cutting out intermediaries and automating processes, blockchain technology can lead to significant cost savings in various industries, such as finance and supply chain management.
Disadvantages of blockchain technology:
Scalability Issues:
Most public blockchain networks face scalability challenges, limiting the number of transactions they can process per second. This can result in slow confirmation times and high transaction fees during periods of heavy usage.
Energy Consumption:
Proof-of-work (PoW) blockchains, such as Bitcoin, are known for their energy-intensive mining processes. This has raised environmental concerns, as it requires substantial computational power.
Lack of Regulation:
The absence of clear and consistent regulations for blockchain and cryptocurrencies in many jurisdictions can create legal uncertainties and compliance challenges.
Irreversible Transactions:
While immutability is a strength, it can also be a disadvantage. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be undone. This can be problematic in cases of accidental or fraudulent transactions.
Privacy Concerns:
Public blockchains are transparent, making all transactions visible to anyone. This can raise privacy concerns, especially for individuals or entities that require confidentiality.
Complexity:
Developing and maintaining blockchain applications can be complex and requires specialized knowledge. This can be a barrier to entry for some businesses and individuals.
Storage and Bandwidth Requirements:
Running a full node on a blockchain network can require significant storage space and bandwidth. This can be a challenge for smaller participants in the network.
Steps to Get Started with Blockchain Technology
- Educate Yourself: Start by educating yourself about the fundamentals of blockchain technology. You can find numerous online courses, articles, books, and videos that explain the concepts and mechanics of blockchain. Understanding the basics is crucial before diving into more complex aspects.
- Select a Blockchain Platform: A variety of blockchain platforms are at your disposal, each with unique features and functionalities.Some popular options include Ethereum, Hyperledger, and Binance Smart Chain. Research these platforms to determine which one aligns with your goals and interests.
- Set Up a Cryptocurrency Wallet: To interact with blockchain networks and perform transactions, you’ll need a cryptocurrency wallet. Wallets are available in different formats, such as internet, hardware, and software wallets.Select a wallet that suits your needs, ensuring it supports the specific blockchain platform you’re interested in.
- Obtain Cryptocurrency: Many blockchain platforms require a specific cryptocurrency to participate in their network. For example, Ethereum uses Ether (ETH). Acquire the necessary cryptocurrency through a cryptocurrency exchange. Ensure that it is safely kept in your wallet.Join Online Communities: Engage with online blockchain communities, forums, and social media groups. Platforms like Reddit, Telegram, and Twitter host active blockchain communities where you can ask questions, share insights, and learn from experienced enthusiasts and professionals.
- Experiment with Small Transactions: Start with small-scale transactions to get a hands-on understanding of how blockchain technology works. You can send cryptocurrency between wallets, interact with decentralized applications (DApps), or participate in blockchain-based games. This practical experience will enhance your knowledge and confidence.
- Stay Updated: Blockchain technology is continually evolving. To stay informed about the latest developments, subscribe to blockchain-related news outlets, blogs, and newsletters. Following reputable influencers and experts on social media can also help you keep up with industry trends.
- Explore Blockchain Projects: Research and explore blockchain projects that align with your interests. Whether you’re intrigued by decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), supply chain solutions, or other applications, there are various projects and startups in each sector. Consider participating in initial coin offerings (ICOs) or token sales if you want to invest in a specific project.
- Consider Further Learning: If your interest in blockchain technology deepens, consider taking more advanced courses or pursuing certifications related to blockchain development, smart contract programming, or blockchain security. These skills can open doors to career opportunities in the blockchain industry.
- Network and Collaborate: Connect with professionals and enthusiasts in the blockchain space. Attend blockchain conferences, seminars, and meetups to expand your network. Collaboration and partnerships can lead to exciting projects and opportunities in the blockchain ecosystem.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is reshaping industries and offering new possibilities. Its decentralized and secure nature makes it a promising technology for the future. As you continue to explore this exciting field, you’ll find that the applications and opportunities are vast. Whether you’re interested in investing, developing, or just learning more, blockchain is a technology worth keeping an eye on.
FAQs
Is blockchain only used for cryptocurrencies?
Blockchain isn’t just for cryptocurrencies; it may be used in a variety of businesses
Is blockchain technology safe?
Blockchain is considered secure due to its decentralized and cryptographic features.
How can I invest in blockchain technology?
You can invest in cryptocurrencies or blockchain-related stocks.
Is blockchain technology secure?
Blockchain is considered secure due to its decentralized and cryptographic features. Once data is added to the blockchain, it is nearly impossible to alter or delete.
Can I invest in blockchain technology?
Yes, you can invest in blockchain technology by purchasing cryptocurrencies or investing in blockchain-related stocks.Make sure you are aware of the risks and conduct thorough research.
What are smart contracts, and how do they work?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that have their terms encoded directly into the code. They don’t require middlemen; they run automatically when certain conditions are met.
What are the environmental concerns related to blockchain technology?
Some blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin, have raised concerns about their energy consumption. The process of mining requires significant computational power, which can impact the environment.
What is blockchain interoperability?
Blockchain interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate and work together. It aims to create a standardized framework for data transfer and transactions between multiple blockchains.
How can I get started with blockchain technology?
To get started, you can educate yourself about blockchain fundamentals, choose a blockchain platform, set up a cryptocurrency wallet, obtain cryptocurrency, join online communities, experiment with small transactions, stay updated, and explore blockchain projects.




One Comment