The Power of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP):Unlocking Efficiency and Growth

Are you looking to propel your business into the future while streamlining operations and boosting efficiency? Look no further than Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. In today’s fast-paced business landscape, ERP has become a cornerstone for organizations seeking to integrate and manage their core business processes. Let’s delve into the world of ERP, exploring its key components, benefits, challenges, and the path to successful implementation.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Sustained success in the fast-paced world of business requires staying ahead of the curve.Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) serves as a powerful tool to achieve just that. But what exactly is ERP? Simply put, ERP is a software solution that enables organizations to integrate and manage their key business processes in a centralized system.
Key Components of ERP Systems
ERP systems encompass a range of modules, each catering to different aspects of business operations. These include Financial Management, Human Resource Management, Supply Chain Management, Inventory Management, and Customer Relationship Management. By seamlessly integrating these components, ERP streamlines workflows and facilitates better decision-making.
Benefits of ERP Implementation
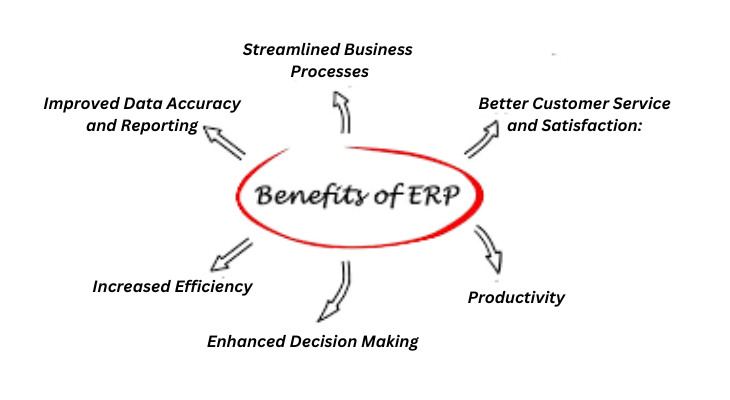
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system offers numerous benefits to organizations across various industries. Here are some key advantages of ERP implementation:
Streamlined Business Processes:
- ERP systems integrate disparate business functions and streamline processes across departments such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and sales. By automating workflows and eliminating manual tasks, ERP enhances operational efficiency and productivity.
Improved Data Accuracy and Reporting:
- ERP centralizes data from different sources into a single database, ensuring data consistency, accuracy, and integrity. With real-time access to reliable data, organizations can generate timely and accurate reports for informed decision-making and regulatory compliance.
Enhanced Decision Making:
- ERP systems provide decision-makers with access to comprehensive, up-to-date information and insights across all areas of the business. By analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and trends, managers can make informed decisions quickly and effectively to drive business growth and profitability.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity:
- By automating repetitive tasks, reducing manual errors, and optimizing workflows, ERP improves overall efficiency and productivity within the organization. Employees can focus on value-added activities rather than administrative tasks, leading to higher output and performance.
Better Customer Service and Satisfaction:
- ERP enables organizations to deliver better customer service and support by providing a 360-degree view of customer interactions, preferences, and history. With access to accurate and timely information, employees can respond promptly to customer inquiries, resolve issues efficiently, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Cost Savings:
- While the initial investment in ERP implementation may be significant, the long-term cost savings can outweigh the expenses. ERP systems help streamline processes, reduce inventory carrying costs, minimize errors, and optimize resource utilization, leading to cost savings and improved profitability over time.
Scalability and Flexibility:
- ERP systems are designed to scale with the growth of the organization and adapt to changing business requirements. Whether expanding operations, adding new products or services, or entering new markets, ERP provides the flexibility and scalability needed to support business growth and expansion
Challenges in ERP Implementation
While the benefits of ERP are substantial, implementing it comes with its own set of challenges:
High Initial Costs:
- One of the primary challenges of ERP implementation is the high initial costs associated with software licensing, hardware infrastructure, customization, training, and consulting services. Budget constraints can pose a significant barrier to implementing an ERP system, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses.
Resistance to Change:
- Resistance from employees to adopt new processes and technologies is another challenge in ERP implementation. Employees may be accustomed to existing workflows and reluctant to embrace change, leading to decreased productivity and morale. Effective change management strategies and employee training are essential to overcoming resistance to change.
Integration Issues:
- Integrating an ERP system with existing systems and databases can be complex and challenging. Compatibility issues, data migration errors, and technical limitations may arise during the integration process, leading to delays and disruptions in operations. Organizations must carefully plan and execute integration to ensure seamless data flow and functionality across systems.
Data Security Concerns:
- Data security is a critical concern in ERP implementation, especially given the sensitive nature of the data managed by ERP systems. Protecting confidential information such as financial data, customer records, and intellectual property from security breaches, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access is paramount. Implementing robust security measures, encryption protocols, access controls, and regular security audits are essential to safeguarding data integrity and confidentiality.
Lack of ERP Expertise:
- Specialized knowledge and expertise are needed for the implementation and management of an ERP system.Organizations may lack in-house resources with the necessary skills and experience to oversee the implementation process effectively. Engaging external consultants, training employees, and investing in ERP expertise are essential steps to mitigate this challenge and ensure successful ERP implementation.
ERP modules:

Financial Management Module:
- Financial transactions are managed by this module, which includes general ledger, accounts payable, and accounts receivable budgeting, and financial reporting. It helps organizations track and manage their finances accurately and efficiently.
Human Resource Management (HRM) Module:
- The HRM module handles all aspects of human resource management, such as employee data management, payroll processing, benefits administration, recruitment, performance management, and training. It streamlines HR processes and ensures compliance with labor regulations.
Supply Chain Management (SCM) Module:
- The SCM module oversees the entire supply chain process, from procurement and inventory management to order fulfillment and distribution. It enables organizations to optimize their supply chain operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
Inventory Management Module:
- This module tracks and manages inventory levels, locations, and movements within the organization. It helps organizations minimize stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and optimize inventory turnover for better cash flow management.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Module:
- The CRM module manages customer interactions and relationships throughout the customer lifecycle. It includes features such as lead management, sales automation, marketing campaigns, customer service, and support. It helps organizations attract, retain, and delight customers for long-term success.
ERP Best Practices:
Thorough Planning and Preparation:
- Before embarking on ERP implementation, organizations should conduct thorough planning and preparation. This includes defining project objectives, identifying stakeholders, assessing business requirements, and establishing a realistic timeline and budget.
Executive Sponsorship and Leadership:
- Executive sponsorship and leadership are critical for the success of ERP projects. Top management should champion the initiative, provide clear direction, allocate resources, and actively support the implementation process to ensure organizational buy-in and commitment.
Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- ERP implementation involves multiple departments and stakeholders across the organization. Encouraging cross-functional collaboration and communication is essential to aligning business processes, addressing diverse needs, and driving consensus on key decisions.
Selecting the Right ERP Solution:
- Choosing the right ERP solution is paramount to success. Organizations should evaluate ERP vendors based on factors such as functionality, scalability, industry expertise, support services, and total cost of ownership. Selecting a solution that aligns with business objectives and requirements is crucial.
Customization vs. Standardization:
- Strike a balance between customization and standardization when configuring the ERP system. While customization may address specific business needs, excessive customization can lead to complexity, cost overruns, and maintenance challenges. Opt for standard features and workflows whenever possible and customize only when necessary.
Comprehensive Training and Education:
- Provide comprehensive training and education to users at all levels of the organization. Training programs should cover ERP functionality, best practices, and workflows relevant to each user’s role. Continuous education and support are essential to ensuring user adoption and maximizing the benefits of ERP.
Effective Change Management:
- Implementing ERP frequently necessitates considerable adjustments to job descriptions, roles, and company procedures.Implementing effective change management strategies, such as communication plans, stakeholder engagement, and user feedback mechanisms, helps minimize resistance to change and facilitate smooth transition.
Data Quality and Governance:
- Ensure data quality and governance throughout the ERP lifecycle. Establish data management policies, standards, and procedures to maintain data integrity, accuracy, and security. Regular data audits and quality checks are essential to ensure the reliability of information generated by the ERP system.
Continuous Improvement and Optimization:
- ERP deployment is a continuous process rather than a one-time occurrence.Encourage a culture of continuous improvement and optimization by soliciting user feedback, monitoring system performance, identifying areas for enhancement, and implementing incremental updates and upgrades as needed.
Future Trends in ERP
Absolutely, here are some future trends in the world of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP):
Cloud-Based ERP Solutions:
- Cloud-based ERP systems are becoming more and more well-liked because of their affordability, scalability, and flexibility.Businesses are increasingly opting for cloud-based ERP systems as they offer easier access, reduced infrastructure costs, and seamless updates.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in ERP:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing ERP by enabling predictive analytics, automation of repetitive tasks, and intelligent decision-making. AI-powered ERP systems can analyze vast amounts of data to provide valuable insights and enhance efficiency.
Blockchain Technology Integration in ERP Systems:
- Blockchain technology is being integrated into ERP systems to enhance data security, transparency, and traceability. By leveraging blockchain, ERP systems can ensure the integrity of transactions, streamline supply chain processes, and mitigate the risk of data tampering or fraud.
Steps for Successful ERP Implementation
Planning Phase:
- Define Goals: Clearly outline the objectives and expected outcomes of the ERP implementation project.
- Assess Requirements: Identify the specific needs and challenges of your organization that the ERP system should address.
- Develop a Comprehensive Plan: Create a detailed project plan that includes timelines, milestones, resource allocation, and budgeting.
System Selection:
- Evaluate ERP Vendors: Research and evaluate different ERP vendors based on factors such as functionality, scalability, industry expertise, and cost.
- Consider Customization Options: Assess the flexibility of the ERP system to customize and adapt to your organization’s unique requirements.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders, including department heads and end-users, in the selection process to ensure buy-in and alignment with organizational goals.
Implementation Phase:
- Configure the System: Customize the ERP system to align with your organization’s workflows, processes, and business rules.
- Data Migration: Transfer existing data from legacy systems to the new ERP system while ensuring data integrity and accuracy.
- Conduct Thorough Testing: Perform comprehensive testing of the ERP system to identify and address any issues or bugs before deployment.
Training and Education:
- Provide Training: Offer training programs and workshops to educate employees on how to use the new ERP system effectively.
- Foster Adoption: Encourage user adoption by demonstrating the benefits of the ERP system and providing ongoing support and assistance.
Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support:
- Launch the System: Deploy the ERP system in a phased approach or all at once, depending on the organization’s readiness and preferences.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously monitor the performance of the ERP system and address any issues or challenges that arise post-implementation.
- Provide Ongoing Support: Offer post-implementation support and maintenance services to ensure the smooth functioning of the ERP system and address any user queries or concerns.
Conclusion
ERP is a game-changer for businesses looking to thrive in today’s competitive landscape. By harnessing the power of ERP, organizations can streamline operations, improve decision-making, and achieve sustainable growth. Embrace ERP, unlock your potential, and pave the way for a successful future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about ERP
What is the typical timeline for ERP implementation?
The timeline for ERP implementation can vary depending on factors such as the size of the organization, complexity of processes, and chosen ERP solution. Implementation can take several months to a year or longer on average.
How can companies make sure that data is secure when implementing ERP?
Data security during ERP implementation is crucial. Businesses can ensure security by implementing encryption protocols, access controls, regular security audits, and employee training on data protection best practices.
What are the common challenges faced during ERP integration?
Common challenges during ERP integration include resistance to change from employees, data migration issues, system compatibility issues, and ensuring seamless integration with existing systems and processes.
How does ERP customization work to fit specific business needs?
ERP customization involves tailoring the ERP system to meet the specific needs and requirements of a business. This can include customizing workflows, reports, and interfaces to align with unique business processes and goals.
What are the key considerations when choosing an ERP vendor?
When selecting an ERP vendor, businesses should consider factors such as the vendor’s reputation, experience in the industry, scalability of the ERP solution, ongoing support and maintenance services, and total cost of ownership over the long term.