Cloud Computing: Types, Providers, and Security

Cloud computing is transforming the way businesses operate and individuals access data and services. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of cloud computing, exploring its various aspects, types, security measures, and future trends. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of what cloud computing is, how it works, and how to navigate the cloud landscape.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Cloud Computing?
The delivery of various services via the Internet is known as cloud computing. Data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software are a few examples of the tools and applications that fall under this category.
With cloud-based storage, files can be saved to a remote database instead of being stored on a local or proprietary hard disk. An electronic gadget can obtain data and the software needed to run it as long as it can connect to the internet.
Many factors make cloud computing a popular choice for individuals and companies, including lower costs, more productivity, speed and efficiency, performance, and security.
Understanding Cloud Computing
Because the data being accessed is located remotely in the cloud or another virtual environment, cloud computing gets its name. Users can store files and programs on faraway servers and access all of the data through the Internet thanks to companies who offer cloud services. This implies that the user can access it remotely because they are not confined to a physical location.
With cloud computing, all of the labor-intensive data processing and crunching is done off of the device you carry around or use to work at. It also transfers all of the work to massive internet computer clusters located far away. Your data, work, and apps are accessible from any device that can connect to the Internet, anywhere in the globe, as the Internet transforms into the cloud.
What kinds of services are available through cloud computing?
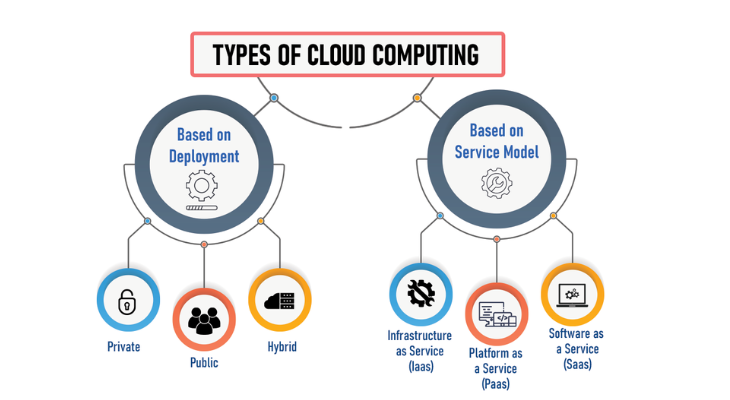
Three general service delivery categories, or types of cloud computing, can be distinguished from one another:
- IaaS. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) providers, like Amazon Web Services (AWS), offer storage and virtual server instances in addition to application programming interfaces (APIs) that enable users to move workloads to virtual machines (VMs). Users may launch, stop, access, and configure the virtual machine (VM) and storage as they see fit. They are also allotted a certain amount of storage. IaaS providers allow for instance customisation and offer small, medium, big, extra-large, memory- or compute-optimized instances for different workload requirements. For commercial users, the IaaS cloud concept is most similar to a remote data center.
- PaaS. Cloud providers host development tools on their infrastructures under the PaaS concept. APIs, web portals, or gateway software are used by users to access these tools online. PaaS is used for general software development, and after the software is built, it is hosted by numerous PaaS providers. AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, and Salesforce’s Lightning Platform are examples of common PaaS products.
- SaaS. Web services, also known as software as a service (SaaS) is a distribution model that makes use of the internet to deliver software applications. A computer or mobile device with internet connectivity can be used by users to access SaaS apps and services from any place. Users can obtain databases and application software under the SaaS model. Microsoft 365, which offers email and productivity features, is a popular illustration of a software as a service (SaaS).
Types of cloud computing
No single kind of cloud computing is appropriate for every situation, nor are all clouds created equal. A variety of models, varieties, and services have developed to help provide the best option for your requirements.
Prior to implementing your cloud services, you must choose the kind of cloud deployment, or cloud computing architecture, that will be used. Utilizing a public, private, or hybrid cloud are the three methods available for implementing cloud services. Study up on cloud computing—public, private, and hybrid.
Public cloud
Third-party cloud service providers, who offer computing resources like servers and storage over the internet, own and run public clouds. One instance of a public cloud is Microsoft Azure. The cloud provider owns and manages all of the hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure in a public cloud. A web browser is used to manage your account and access these services.
Private cloud
Cloud computing services utilized only by one company or organization are referred to as private clouds. On the business’s on-site datacenter, a private cloud may be physically situated. Additionally, some businesses pay outside service providers to host their private clouds. A private cloud is one where the infrastructure and services are kept up to date on a private network.
Hybrid cloud
Because of technology that enables data and applications to be transferred across them, hybrid clouds combine the capabilities of private and public clouds. With a hybrid cloud, your company can benefit from increased flexibility and deployment options as well as improved infrastructure, security, and compliance by enabling data and apps to flow between private and public clouds.
Types of Cloud Services
Whatever the type of service, cloud computing offers users a number of advantages, such as:
- Data retrieval, backup, and storage
- Developing and examining apps
- examining data
- Streaming video and audio
- On-demand software delivery
Despite being a relatively new service, cloud computing is already being used by a wide range of organizations, including government agencies, small and medium-sized enterprises, nonprofits, and even private individuals.
Cloud computing deployment models
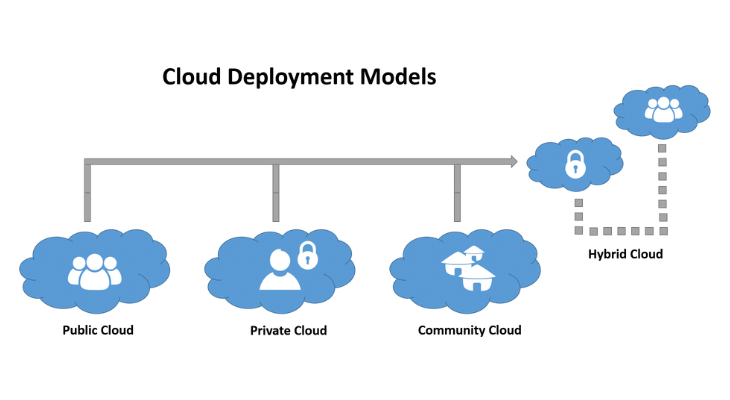
The cloud service under the public cloud model is provided online by a third-party cloud service provider (CSP). While many public cloud services offer long-term commitments, most are sold on an as-needed basis, usually by the minute or hour. Consumers only pay for the bandwidth, storage, and central processing unit cycles that they actually use. AWS, Microsoft Azure, IBM, Tencent, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are some of the top public cloud service providers (CSPs).
Internal users receive private cloud services from a company’s data center. An enterprise creates and manages its own underlying cloud architecture while using a private cloud. This paradigm maintains the administration, control, and security typical of local data centers while providing the flexibility and ease of use of the cloud. IT chargeback may or may not be used to invoice internal users for services rendered. Typical private cloud providers and technologies are OpenStack and VMware.
A hybrid cloud combines on-premises private cloud infrastructure with public cloud services, allowing orchestration and automation between the two. Businesses can use the public cloud to manage workload bursts or demand spikes while running sensitive apps or mission-critical workloads on the private cloud. Creating a unified, automated, and scalable environment that leverages the full potential of public cloud infrastructure is the aim of a hybrid cloud, all while preserving control over mission-critical data.
Additionally, using numerous IaaS providers, or a multi-cloud architecture, is becoming more and more popular among enterprises. Applications can now move between several cloud providers or even run simultaneously on two or more cloud providers thanks to this.
Businesses use several clouds for a variety of reasons. They might take this action, for instance, to reduce the possibility of a cloud service interruption or to benefit from a specific provider’s more affordable prices. Because cloud providers’ offerings and APIs differ, developing applications and implementing multi-cloud can be difficult.
However, as providers’ services and APIs converge and become more standardized through industry initiatives like the Open Cloud Computing Interface, multi-cloud installations ought to get easier.
A community cloud, which is shared by multiple enterprises, serves a specific community with similar issues, such as those related to mission, policy, security, and compliance. A community cloud can be located on or off campus and is either run by these companies or by an outside vendor.
Uses of cloud computing

It’s likely that you are utilizing cloud computing even if you are unaware of it. Cloud computing is probably at work behind the scenes whenever you use an online service for email, document editing, video or TV viewing, music streaming, gaming, or storing photos and other files. Numerous companies—from small start-ups to multinational
For a variety of reasons, businesses, governments, and nonprofit organizations have embraced cloud computing technology.
A few instances of what can be achieved with cloud services from a cloud provider are as follows:
- Create cloud-native applications:Build, launch, and scale web, mobile, and API applications quickly. Benefit from cloud-native techniques and technologies including DevOps, microservices architecture, containers, Kubernetes, and API-driven communication.
- Store, back up, and recover data:By moving your data online to an offsite cloud storage system that is available from any place and on any device, you can protect your data more affordably and massively.
- Stream audio and video:Engage your audience with global distribution of high-definition video and music at any time, anywhere, on any device.
- Provide software as needed:On-demand software, also referred to as software as a service (SaaS), enables you to provide consumers with the most recent software versions and updates—anytime they need them, wherever they are.
- Test and build applications:Scalable cloud infrastructures facilitate easy upscaling and downscaling, hence reducing application development time and cost.
- Analyze data:In the cloud, unify your data across teams, departments, and geographies. Next, leverage cloud services to find insights for better decision-making, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Embed intelligence:To help engage customers and offer insightful information based on the data collected, use intelligent models.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Using software from any device through a browser or native app is only one of the many advantages that cloud-based software provides to businesses of all sizes. Consequently, users can effortlessly transfer their files and preferences to different devices.
- There is much more to cloud computing than merely allowing file access across several devices. Users can store files with services like Dropbox and Google Drive and check their email on any computer thanks to cloud computing services.56 Users can also back up their files, music, and photos with cloud computing services, making sure those files are instantly accessible in the event of a hard drive crash.
- It also has enormous potential to save costs for large businesses. Prior to the cloud becoming a practical substitute, businesses had to invest in, build, and maintain expensive infrastructure and information management technology. Fast Internet connections allow businesses to replace expensive server centers and IT personnel with online workspaces where staff members engage with the cloud to accomplish their work.
- People can save up storage space on their laptops or desktop computers thanks to the cloud architecture. Additionally, because software businesses can now sell their products online instead of through more conventional, tangible channels like discs or flash drives, customers can upgrade software more quickly. Customers of Adobe, for instance, can access the Creative Cloud’s apps through an Internet-based subscription.7 This makes it simple for users to receive updates and repairs for their software.
Disadvantages of the Cloud Computing
- Cloud security has always been a major worry, particularly when it comes to private financial and medical data. Although laws compel cloud computing companies to strengthen their security and compliance protocols, the problem still exists. Important data is protected by encryption, but if the encryption key is lost, the data is also lost.
- Cloud computing firms’ servers can be affected by power outages, internal problems, and natural calamities. The geographic reach of cloud computing is bidirectional: a California blackout could render customers in New York immobile, and a Texas-based company could lose its data in the event that its Maine-based supplier went down.
- Like any new technology, managers and staff must adjust to a learning curve. However, accidental errors can propagate throughout a whole system when numerous users access and alter data via a single portal.
Conclusion
To sum up, cloud computing is a dynamic and revolutionary technology that is reshaping the internet. The fundamentals, kinds, essential elements, security, use cases, difficulties, and upcoming trends have all been discussed. You’ll be more capable of utilizing the cloud and making wise choices about its uses in your personal and professional life if you have this information.
This post seeks to be a helpful resource for anyone wishing to learn about cloud computing in an approachable and interesting way by covering a variety of LSI keywords, offering educational information, and optimizing keywords for search engines.
FAQs: Cloud Computing
What are cloud computing’s main advantages?
Cost savings, scalability, flexibility, automated upgrades, and pay-as-you-go resource access are just a few benefits the cloud computing model offers. It also lessens the requirement for internal maintenance and infrastructure.
Which kinds of cloud computing services are there?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) are the three main service models that make up cloud computing. The degree of authority and accountability vested in the user or organization varies among these types.
How can I pick the cloud service provider that best suits my requirements?
The best cloud service provider for you will rely on your unique needs. A few things to think about are the services offered by the supplier, costs, locations of the data centers, security protocols, and customer assistance. Prior to choosing a choice, it is critical to evaluate the objectives and needs of your company.
What safeguards are in place to keep data safe in the cloud?
Cloud providers employ a range of security protocols, such as access controls, identity and access management, encryption of data, and adherence to industry standards. It’s critical to comprehend the security features provided by the provider of your choice and to apply best practices yourself.
Which difficulties come with using cloud computing?
Potential downtime, issues with data protection and ownership, and the requirement for dependable internet connectivity are some of the difficulties associated with cloud computing. Addressing adherence to data privacy laws is also crucial.





2 Comments