Big Data Analytics | Types and Tools

Big data Analytics is the driving force behind some of the most important industry breakthroughs in the digital world today, whether they are applied in the finance, government, health care, or other sectors. Continue reading to learn more about the numerous advantages of big data analytics.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Big Data Analytics
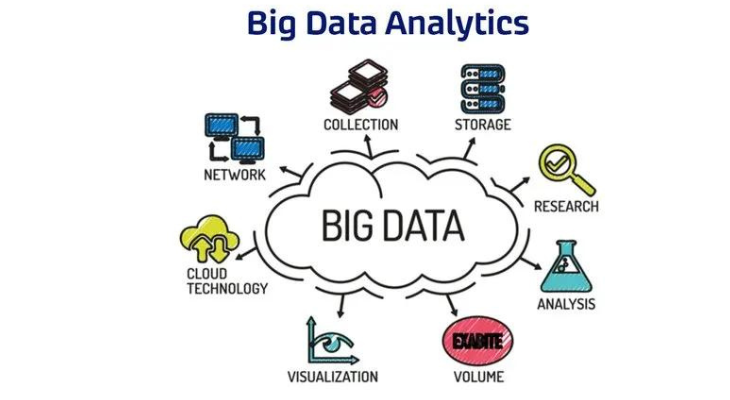
The often difficult process of analyzing large amounts of data to find patterns, correlations, market trends, and customer preferences that can assist businesses in making wise decisions is known as big data analytics.
In general, data analytics tools and methods enable firms to examine large data sets and extract fresh insights. Basic inquiries concerning the performance and operations of businesses are addressed by business intelligence (BI) queries.
Advanced analytics, which includes sophisticated applications with components like statistical algorithms, what-if analysis, and predictive models driven by analytics systems, is known as big data analytics.
Why is big data analytics important?
Big data analytics tools and systems enable organizations to make data-driven decisions that enhance business-related results. Improved operational efficiency, increased revenue potential, consumer personalization, and more successful marketing are possible advantages. These advantages can provide you an advantage over competitors if you use an effective strategy.
Types of big data analytics (+ examples)

Big data analytics comes in four primary forms that help and guide various business choices.
1.Descriptive analytics
Easily readable and interpretable data is what is meant by descriptive analytics. With the use of this data, reports and information visualizations detailing a company’s sales and profits can be produced.
As a Example, a well-known pharmaceutical business analyzed data from its offices and research facilities throughout the epidemic. They identified underutilized areas and departments that were merged with the use of descriptive analytics, saving the business millions of dollars.
2.Diagnostics analytics
Diagnostic analytics enables businesses to determine the root cause of an issue. Big data tools and technology enable users to mine and retrieve data that aids in problem analysis and helps stop problems from happening again.
Example: Despite customers continuing to add goods to their shopping carts, the sales of a clothing company have fallen. It was discovered using diagnostic analytics that the payment page was malfunctioning for a few weeks.
3.Predictive analytics
To develop forecasts, predictive analytics examines both historical and current data. Users can examine the data to forecast market trends by using machine learning, data mining, and artificial intelligence (AI).
For Example, in the manufacturing industry, businesses can forecast whether or not a piece of equipment would malfunction or break down by using algorithms based on prior data.
4.Prescriptive analytics
By using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to collect data and use it for risk management, prescriptive analytics offers a solution to an issue.
As an example, utility firms, gas producers, and pipeline owners in the energy industry identify variables that impact the price of gas and oil in order to manage risks.
Tools used in big data analytics
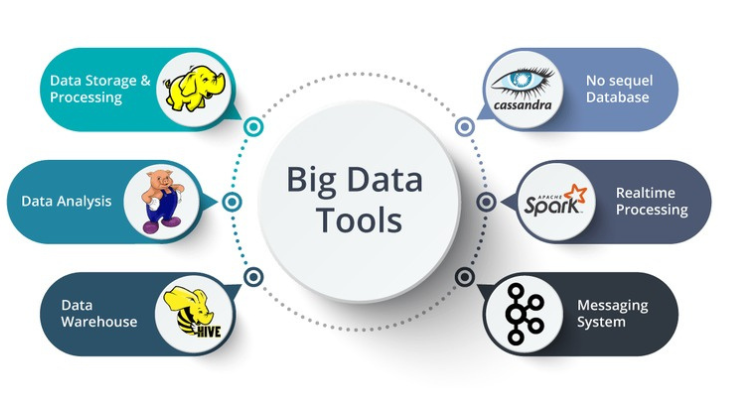
To make use of all that data, instruments are needed. Thank goodness, data analysts may now choose from a wide variety of user-friendly software programs thanks to technological advancements.
- Hadoop: A huge data processing and storing open-source framework. Both structured and unstructured data can be handled and analyzed with Hadoop.
- Spark: A cluster computing framework that is open-source and utilized for real-time data processing and analysis.
- Applications that simplify large data across several platforms, including MongoDB, Apache, Hadoop, and Amazon EMR, are known as data integration software.
- Tools for stream analytics: Programs that combine, filter, and evaluate data that may be kept on many platforms and file formats, like Kafka.
- Distributed storage: Databases like Cassandra that can divide data among several servers and can detect lost or corrupted data.
- Hardware and software for predictive analytics: Systems that analyze vast volumes of complicated data and forecast future events (such as fraud detection, marketing, and risk assessments) using machine learning and algorithms.
- Tools for data mining: Applications that let users search through large amounts of organized and unstructured data.
- Non-relational data management systems, or NoSQL databases, are perfect for handling unstructured and raw data.
- Data warehouses: Locations where vast volumes of information are gathered from many sources and stored, usually according to pre-established schemas.
Familiarizing yourself with big data analytics tools
It’s crucial to understand how to use industry-standard tools like the ones listed above. You can acquire online experience with frequently utilized tools whether you’re looking to develop in your career or are just trying to get a better position. Here are some pertinent choices to think about:
- Overview of Big Data Using Spark and Hadoop
- Specialization in Big Data and Machine Learning on Google Cloud
- GCP Specialization in Data Engineering, Big Data, and Machine Learning
- PostgreSQL as a General-purpose Database
Benefits and Advantages of Big Data Analytics
1.Risk Management
Use Case: The Philippine banking institution Banco de Oro employs big data analytics to spot irregularities and fraudulent activity. The company uses it to reduce the number of potential suspects or issues’ underlying causes.
2.Product Innovation and Development
Use Case: Rolls-Royce, one of the world’s leading producers of jet engines for use by military forces and airlines, using big data analytics to assess the effectiveness of its engine designs and determine whether any changes are necessary.
3.Organizational Decision-Making That Is Faster and Better
Use Case: Starbucks makes strategic decisions by utilizing Big Data analytics. For instance, the business uses it to determine whether or not a specific area would be a good fit for a new outlet. They will examine a number of variables, including accessibility to the site, population, and demographics.
4.Improve Customer Experience
Use Case: To enhance client experiences, Delta Air Lines employs big data analysis. They keep an eye on tweets to learn about the experiences of their clients with regard to travel, delays, and other issues. When an airline sees bad tweets, it takes the appropriate action to address the issue. The airline is able to foster positive customer connections by openly addressing these problems and providing remedies
The Stages of Big Data Analytics Lifecycle

Let’s now recap the operation of big data analytics:
- Stage : Business case evaluation – A business case, which outlines the purpose and rationale for the study, is the first step in the Big Data analytics lifecycle.
- Stage : Data Identification – A wide range of data sources are identified in this step.
- Stage : Data Filtering: Here, all of the previously detected data is filtered to get rid of any corrupt data.
- Stage : Data extraction: Information that is incompatible with the tool is taken out and converted to an appropriate format.
- Stage:Data with identical fields from several datasets are combined in stage five, which is known as data aggregation.
- Stage : Data analysis – To find relevant information, data is assessed using statistical and analytical methods.
- Stage : Data Visualization – Big Data analysts can create graphical representations of the analysis using programs like Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView.
- Stage : Final analysis result – This is the last stage in the Big Data analytics lifecycle, where business stakeholders who plan to take action are given access to the analysis’s final results.
Conclusion on Big Data Analytics:
To sum up, big data analytics is becoming an essential part of contemporary corporate plans and decision-making procedures. It gives businesses the ability to manage the massive volumes of data produced every day and transform it into useful insights that boost productivity, creativity, and competitiveness. There are a plethora of possible advantages, such as better client experiences, more effective product development, financial savings, and the capacity for data-driven prediction.
Big Data Analytics FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions):
Big Data Analytics: What Is It?
The technique of looking through huge, complicated databases to find hidden trends, insights, and patterns is known as big data analytics. It entails utilizing a variety of instruments and methods to wrest useful information from massive volumes of data.
Why is Big Data Analytics important?
Big Data analytics is crucial because it gives businesses a competitive edge, enhances operational effectiveness, and enables data-driven decision-making. It may result in improved cost optimization, product development, and consumer comprehension.
Which sectors gain from big data analytics?
Big Data analytics has applications in almost every industry, including manufacturing, banking, healthcare, retail, and entertainment. Applications for it include marketing, detecting fraud, improving healthcare results, and more.
What distinguishes traditional data analysis from big data?
Big Data refers to extraordinarily vast and varied datasets that are difficult to handle or evaluate using conventional technologies. For processing and analysis, specialist technologies like Hadoop and Spark are needed.
Which big data analytics tools are in demand?
Big Data analytics often uses tools like Hadoop, Spark, Apache Flink, and NoSQL databases. For data visualization, business intelligence solutions like Tableau and Power BI are also well-liked.
How can businesses guarantee Big Data security and privacy?
Access restrictions, data governance regulations, and robust data encryption can all be implemented by businesses. It is essential to comply with data protection laws like GDPR and conduct routine audits.