Cryptocurrency: How its work

If you’ve heard the buzz around “Cryptocurrency” but aren’t quite sure what it’s all about, you’re in the right place. We’ll delve deeply into the intriguing world of cryptocurrencies in this post, covering everything from the fundamentals to the most recent developments. You will have a firm understanding of all you need to know to begin using cryptocurrencies by the time you finish reading this.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Cryptocurrency?

Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that relies on cryptographic techniques for security. Cryptocurrencies run on distributed ledger technology, or blockchain, which is decentralized and distributed, in contrast to traditional currencies that are issued and controlled by governments or central banks. Peer-to-peer transactions are made easier by this innovative kind of money, which is uncontrolled by a single entity.
Pseudonymous wallet addresses are used by the blockchain to guarantee user anonymity while recording and verifying all cryptocurrency transactions. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum have become very popular, not just as digital assets but also as a way to conduct transactions and fuel cutting edge technology like decentralized applications and smart contracts. Cryptocurrencies are a game-changing force in the finance and technology industries because of their decentralized structure and potential for financial inclusion.
How does Cryptocurrency work?

Blockchain is a decentralized, secure digital ledger system that powers cryptocurrency. It eliminates the need for middlemen like banks, which simplifies transactions. When a bitcoin transaction is started, its details are disseminated around the network, validated by nodes, and then compiled by miners into a block. In order to add the block to the blockchain, these miners compete to solve challenging mathematical puzzles, a process known as mining. Transactions are clear and permanent once added.
Digital wallets are used by users to store their bitcoin, and private keys are used to approve transactions. Cryptocurrencies function independently of centralized authority and provide accessibility, security, and the possibility of international peer-to-peer transactions. This cutting-edge technology has the power to revolutionize conventional banking and open up new opportunities in the digital economy.
Types of Cryptocurrency?
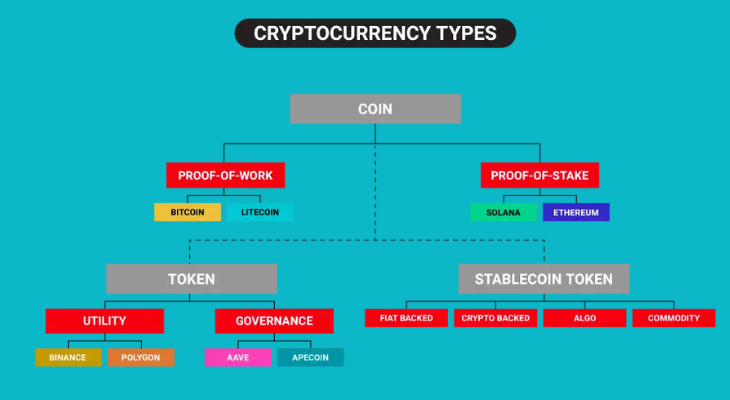
Store of Value:
- Bitcoin (BTC): Also known as “digital gold,” Bitcoin is mostly utilized as an inflation hedge and a store of value
Smart Contract Platforms:
- Ethereum (ETH): Ethereum is well-known for allowing the development of decentralized apps (DApps) through the use of smart contracts.
Digital Payment Coins:
- Ripple (XRP): Ripple is a platform that facilitates international money transfers and was created for quick cross-border payments.
- Litecoin (LTC): Litecoin is used for regular transactions and provides quicker transaction confirmation times.
- Bitcoin Cash (BCH): Bitcoin Cash aims to improve scalability and transaction speed.
Privacy Coins:
- Monero (XMR): By hiding transaction details, Monero aims to improve user privacy.
- Zcash (ZEC): Zcash gives users different levels of privacy by letting them choose between shielded and visible transactions.
Utility Tokens:
- Binance Coin (BNB): Within the Binance ecosystem, Binance Coin is utilized for trading fee discounts and other services.
- Chainlink (LINK): Chainlink offers smart contract decentralized oracle services.
- Polkadot (DOT): Polkadot facilitates interoperability by connecting several blockchains.
Stablecoins:
- Tether (USDT): In a volatile cryptocurrency market, Tether is a stablecoin that is based on the value of a fiat currency, like the US dollar.
- Other stablecoins include TrueUSD (TUSD), Dai (DAI), and USD Coin (USDC).
Security Tokens:
- Tokenized Assets: Security tokens provide a controlled and legal avenue for trading and investing by representing ownership in physical assets such as stocks or real estate.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs):
- NFTs are distinct digital assets that are frequently utilized for virtual real estate, art, games, and collectibles. Examples of these include CryptoKitties, NBA Top Shot, and Decentraland.
Cross-Chain Platforms:
- Cosmos (ATOM): Cosmos is primarily concerned with blockchain interoperability.
- Polkadot (DOT): As previously indicated, the goal of Polkadot is to link several blockchains.
Supply Chain and Verification:
- VeChain (VET): VeChain is primarily concerned with product verification and supply chain management.
- Waltonchain (WTC): This platform is utilized for asset tracking and management.
Examples of Cryptocurrency

- Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most well-known cryptocurrency is called Bitcoin. The main purposes of bitcoin, which is also known as “digital gold,” are as a store of value and a means of trade.
- Ripple (XRP): Designed to ease cross-border transactions, Ripple is a digital payment mechanism. The Ripple network’s native cryptocurrency, XRP, is utilized to supply liquidity for cross-border money transfers.
- Bitcoin Cash (BCH):A fork of Bitcoin created with the intention of resolving scalability difficulties is called Bitcoin Cash (BCH). Larger block sizes allow for quicker and less expensive transactions.
- Cardano (ADA): Cardano is a blockchain platform distinguished by its methodology based on science and research. Its native cryptocurrency, ADA, is utilized for transactions and staking.
- Polkadot (DOT): Polkadot is a multi-chain network that facilitates communication between several blockchains. DOT is employed in bonding, staking, and governance.
- Chainlink (LINK): Chainlink enables smart contracts to communicate with real-world data by offering decentralized oracle services. To reward node operators for providing this data, LINK is employed.
- Stellar (XLM): Stellar is a blockchain platform intended for financial services and international payments. The native money on the Stellar network, XLM, is utilized to make transactions easier.
- Tezos (XTZ): Tezos is a blockchain platform that updates itself using a self-amending protocol. The native cryptocurrency utilized for network governance and staking is called XTZ.
- VeChain (VET) is a blockchain platform that specializes in product verification and supply chain management. Both transactions and the ecosystem are powered by VET.
- Cardano (ADA): Cardano is a blockchain platform distinguished by its methodology based on science and research. Its native cryptocurrency, ADA, is utilized for transactions and staking.
- Filecoin (FIL): Filecoin is a decentralized storage network that allows users to rent and lease unused storage space. Payment for these storage services is made using FIL.
- Solana (SOL): renowned for its quick transaction times and inexpensive fees, Solana is a high-performance blockchain platform. SOL is employed for staking and network operations.
Is Cryptocurrency safe?

The degree of safety associated with cryptocurrency is a complex matter that is primarily determined by the way in which individuals and institutions handle their cryptocurrency holdings. Here are some crucial things to remember:
- Security of Cryptocurrency Wallets: The security of your wallet has a major impact on the security of your cryptocurrency. One of the safest solutions is a hardware wallet, which stores your private keys offline and is therefore less susceptible to hackers. Online and software wallets are convenient, but they can be more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
- Private Key Protection: When it comes to bitcoin ownership, the private key is the most important piece of information. It is imperative that you protect your private key and do not divulge it to anybody. You will always be unable to access your cryptocurrency if you lose your private key.
- Phishing and Scams: People who use cryptocurrencies are susceptible to fraudulent schemes, phishing assaults, and scams. Avoid accepting unsolicited offers and make sure websites, emails, and people promoting freebies or investment possibilities are legitimate.
- Exchange Security: Select reliable platforms with strong security measures while using bitcoin exchanges. To safeguard user assets, a number of well-known exchanges use cold storage of funds, two-factor authentication, and encryption.
- Legal and Regulatory Risks: In many places, cryptocurrency operates in a legal murky area. The safety and legality of utilizing cryptocurrencies may change as a result of changes to laws and regulations. It’s crucial to keep up with changes in the regulatory environment.
- Market Volatility: There is a chance for financial danger due to the extreme volatility of cryptocurrency prices. It’s critical to understand this volatility if you plan to use or invest in cryptocurrencies.
- Scalability and Transaction Speed: A few cryptocurrencies have problems with both of these parameters. Network congestion or slowness can cause expensive or delayed transactions, which compromises usability and security.
- Smart Contract Risks: On blockchain systems such as Ethereum, smart contracts can be used with vulnerabilities that lead to monetary losses due to coding flaws. For security purposes, smart contract audits and verifications are essential.
- Backup and Recovery Plans: It’s critical to have a backup strategy in place in case you misplace your cryptocurrencies. This could include mnemonics, backup keys, and thorough asset documentation.
- Education and Awareness: It’s critical to keep up with security precautions, best practices, and possible hazards. Users who pursue ongoing education can safeguard their cryptocurrency investments and make well-informed judgments.
Four tips to invest in Cryptocurrency safely
- Education and Research:Make the effort to learn about the project, its technology, use case, and the people behind it before investing in any cryptocurrency. Learn about the sentiment of the community and the whitepaper. Steer clear of investing in something you don’t completely understand.
- Use Reputable Exchanges and Wallets:Select reputable cryptocurrency exchanges that offer robust security measures like cold storage of funds and two-factor authentication (2FA). Moreover, store your funds in hardware wallets or other safe bitcoin wallets. Refrain from keeping a lot of cryptocurrency on exchanges because they can be hacked.
- Diversify Your Portfolio:One way to lower risk is to diversify your cryptocurrency holdings. Avoid investing all of your money in a single cryptocurrency. Diversification helps lessen the effects of fluctuations in an asset’s price.
- Stay Informed and Exercise Caution:Keep abreast of market developments and cryptocurrency news. Offers for investments that seem too good to be true or that guarantee profits should be avoided. Be cautious of fraudulent schemes and phishing scams. Refrain from disclosing private keys or personal information to strangers, and be wary of unsolicited offers or correspondence.
Future Trends in Cryptocurrency

- Increased Adoption: The mainstream acceptance of cryptocurrencies is advancing steadily. The increasing recognition of the advantages of digital currencies by individuals, organizations, and institutions is resulting in their wider adoption and utilization.
- Regulation and Compliance: Global regulatory organizations are striving to provide more precise standards for the use of cryptocurrencies as they become more widely accepted. It is anticipated that regulatory clarity will lessen ambiguity and promote institutional involvement.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Many central banks are exploring the creation of their digital currencies. CBDCs have the potential to completely transform the world financial system and provide a regulated substitute for conventional cryptocurrencies.
- Interoperability: A developing trend is the capacity for various blockchains and cryptocurrencies to communicate with one another. Polkadot and Cosmos are two examples of projects that integrate several blockchain networks to improve their functionality and usefulness.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi apps are growing and provide traditional financial intermediary-free services such as borrowing, lending, trading, and yield farming. It’s probable that the DeFi ecosystem will expand and change.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs, which stand for distinct digital assets, are very well-liked in fields including collectibles, gaming, and digital art. It is anticipated that the NFT field would see ongoing innovation and industry convergence.
- Energy-Efficient and Scalable Blockchains: Scalability and energy efficiency have been critical issues for blockchain networks. Future directions will see the creation and acceptance of consensus processes that are more energy-efficient as well as approaches to scaling issues.
- Cross-Border Payments: Because of their affordability and quickness, cryptocurrencies are being utilized for cross-border transactions more and more. Cross-border payments should get increasingly more accessible and efficient as these technologies develop.
- Asset Tokenization: Real-world assets like equities, commodities, and real estate are increasingly being tokenized. This trend has the ability to completely change the purchasing, selling, and trading of assets.
- Privacy Coins and Enhanced Privacy Features: Privacy-focused cryptocurrencies and enhanced privacy features are likely to gain prominence as users seek to protect their financial privacy and data.
- Quantum Computing and Security: The field of cryptocurrencies faces both opportunities and challenges as a result of the development of quantum computing. To maintain long-term security, cryptocurrency initiatives are investigating quantum-resistant cryptography techniques.
- Environmental Considerations: More environmentally friendly consensus processes have been developed as a result of worries about how mining cryptocurrencies may affect the environment. The cryptocurrency industry may become more sustainable as a result of this development.
Conclusion:
The digital era gave rise to cryptocurrency, which has quickly changed the financial industry and beyond. The fundamental tenets of decentralization, security, and accessibility present promising opportunities going forward. But there are several difficulties with cryptocurrencies. Cautious evaluation is required because to its price volatility, regulatory concerns, and technical difficulties.
With trends including growing usage, DeFi innovation, and the possibility of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) influencing its course, the future of cryptocurrencies looks bright. To fully utilize this innovative technology, people and organizations should be educated, proceed with prudence, and give security first priority as the environment changes.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions):
Is cryptocurrency legal?
The legality of cryptocurrencies differs by nation. While some nations have outright banned it, others have put limits on it. It’s important to learn about local restrictions before investing in or utilizing cryptocurrencies.
How can I buy cryptocurrency?
Reputable cryptocurrency exchanges allow you to buy bitcoin with fiat money or other cryptocurrencies. Exchanges like Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken are frequently used.
Which cryptocurrency is the greatest place to invest?
There isn’t a universal solution. Your objectives, risk tolerance, and research will determine which cryptocurrency is best for you to invest in. Although Ethereum and Bitcoin are frequently seen as secure beginning places, diversification is advised.
How do I store my cryptocurrency securely?
Hardware wallets are among the safest ways to store cryptocurrency, however digital wallets that are secure can also be used. Make sure your wallet and private keys are accessible from a backup location.
Are cryptocurrencies taxable?
Country-specific tax laws apply to cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies are taxable in several jurisdictions, including capital gains tax. Seek advice from a tax expert to comprehend your responsibilities.
What is a blockchain?
A distributed, decentralized digital ledger known as a blockchain keeps track of transactions made via a network of computers. It guarantees data immutability, security, and transparency.