Power of Cloud Hosting: Types and Services

Are you ready to explore the world of cloud hosting? It’s a game-changer in the world of IT, offering flexibility, scalability, and endless possibilities. In this article, we’ll take you on a journey through the cloud, helping you understand the concept, its benefits, and how to make the most of it. Plus, we’ll answer your burning questions about cloud hosting. So, let’s get started!
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Cloud Hosting
Imagine having access to your data, applications, and resources from anywhere in the world, securely and effortlessly. That’s the magic of cloud hosting. It’s like having your own digital fortress in the sky, and here’s why it matters.
Cloud hosting is a service that allows businesses and individuals to host their websites, applications, and data on remote servers. These servers are maintained and managed by cloud hosting providers, like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. This concept has gained immense popularity due to the numerous benefits it offers.
Types of Cloud Hosting
When it comes to cloud hosting, you have several options to choose from, each catering to specific needs and preferences. Let’s delve into the main types of cloud hosting and provide examples to illustrate each one:
- Public Cloud:Public cloud hosting is like renting space on a public beach. You share resources with other users, and your data and applications are hosted on servers managed by cloud service providers. It’s a cost-effective and flexible option, making it ideal for startups and small businesses.For Example, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Private Cloud:Private cloud hosting is like having your private island in the digital world. In this setup, cloud resources are dedicated to a single organization, providing maximum control, security, and customization. Private cloud is often chosen by large enterprises with stringent security and compliance requirements.Example: IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, VMware Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud:Hybrid cloud hosting offers the best of both public and private clouds. It combines the advantages of on-premises infrastructure with the scalability and flexibility of public cloud resources. This makes it an excellent choice for businesses that need to balance security and cost-effectiveness.Example: AWS Outposts, Azure Arc, Google Anthos
- Community Cloud:Community cloud hosting is designed for a specific community, such as organizations within the same industry or with shared interests. Members of the community share and manage cloud resources, which can lead to cost savings and collaboration. Example: Salesforce Community Cloud
- Multi-Cloud:Businesses opt for a multi-cloud strategy to avoid vendor lock-in, leverage specific strengths of different providers, and enhance redundancy.Example: Using AWS for storage, Azure for AI, and Google Cloud for data analytics
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing is an event-driven model where you don’t need to manage servers. Cloud providers handle infrastructure for you, allowing you to focus solely on code. It’s ideal for building small, independent functions, which are executed in response to events.Example: AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, Azure Functions
- Function as a Service (FaaS):FaaS is a subset of serverless computing where you write code that performs a single function. It’s designed to run discrete tasks, and you’re only charged for the time your code is executing.Example: AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, Azure Functions
- Containers and Kubernetes:Containers and Kubernetes provide a way to package and orchestrate applications. Containers are portable, lightweight, and can run consistently across various environments, making them ideal for modern application development and deployment.Example: Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS), Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Managed WordPress Hosting:Managed WordPress hosting is a specialized hosting solution designed for WordPress websites. It offers features like automatic updates, security, and performance optimization tailored for WordPress users.Example: WP Engine, Bluehost, SiteGround.
Key Cloud Hosting Providers
When it comes to cloud hosting, you have a variety of providers to choose from, each offering its unique set of services and features. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key players in the cloud hosting industry:
- AWS (Amazon Web Services):Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the undisputed leader in cloud hosting. They provide a vast array of services and solutions for businesses of all sizes. From compute and storage to machine learning and analytics, AWS is known for its scalability, reliability, and global reach. If you’re looking for a well-established and comprehensive cloud hosting provider, AWS is a top choice.
- Azure (Microsoft Azure):Microsoft Azure is Microsoft’s cloud platform, offering a wide range of services that seamlessly integrate with other Microsoft products. Whether you’re running Windows-based applications or need powerful AI and machine learning tools, Azure provides the tools and resources to support your business’s growth.
- Google Cloud:They offer a robust cloud platform with a focus on data-driven solutions. Google Cloud’s global network and developer-friendly tools make it a strong choice for businesses seeking to harness the power of data and innovation.
- IBM Cloud:IBM Cloud provides cloud solutions designed for businesses, with a focus on hybrid cloud environments. They offer a variety of cloud services, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, and are known for their enterprise-grade security and support.
- Oracle Cloud:Oracle Cloud is a cloud service provider that specializes in database solutions and enterprise applications. Their cloud offerings are designed to support businesses with data-intensive workloads, and they emphasize high performance and security.
- Alibaba Cloud:Alibaba Cloud is a leading cloud provider in the Asia-Pacific region and is rapidly expanding globally. They offer a wide range of cloud computing services, and their strength lies in supporting e-commerce, big data, and artificial intelligence applications.
- DigitalOcean:DigitalOcean caters to developers and startups, offering simplicity and ease of use. Their cloud platform focuses on providing virtual private servers (VPS) and developer-friendly tools for deploying and managing applications.
Features and Services
- Virtual Servers:Imagine having the power to create, modify, and scale your servers with just a few clicks. Cloud hosting provides virtual servers (often referred to as instances), allowing you to configure your computing resources according to your needs. This flexibility is ideal for accommodating changing workloads, ensuring your applications run smoothly, and only paying for what you use.
- Scalability:Scalability is one of the most significant advantages of cloud hosting. Whether you’re experiencing a sudden surge in website traffic or expanding your business operations, the cloud can effortlessly scale your resources up or down. This means you’re always prepared to meet demand without overcommitting to hardware that might go unused.
- Data Storage Solutions:Say goodbye to the limitations of physical storage devices. In the cloud, you have access to vast and scalable storage solutions. Store your data, files, and media securely and retrieve them from anywhere in the world. Plus, cloud storage ensures data redundancy and disaster recovery, giving you peace of mind.
- Managed Hosting:Not everyone is an IT expert, and that’s perfectly fine. Cloud hosting providers often offer managed hosting services, where their team of experts takes care of server management, security, updates, and other technical aspects. This frees you up to focus on your core business activities, knowing that your hosting infrastructure is in capable hands.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN):If you have a global audience, a CDN is your best friend. Content Delivery Networks accelerate the delivery of web content to users worldwide. By caching content on servers distributed across the globe, CDNs reduce loading times, improving the user experience and ensuring your content is accessible quickly, no matter where your users are located.
- Database Services:Hosting a database in the cloud offers several advantages, such as high availability, automatic backups, and the ability to scale your database resources as needed. This is crucial for businesses that rely on databases to store and retrieve data efficiently.
- Application Hosting:Cloud hosting isn’t just for websites; you can also host your applications in the cloud. This allows you to easily deploy, manage, and scale applications, making it an ideal choice for software development and deployment.
- DevOps Tools:Cloud hosting providers often offer a range of DevOps tools and services to facilitate software development, testing, and deployment. These tools streamline the development process, promote collaboration, and improve efficiency.
- Analytics and Machine Learning Services:Leverage the power of big data and artificial intelligence with cloud-based analytics and machine learning services. These tools enable you to derive valuable insights from your data, automate tasks, and make data-driven decisions.
- IoT (Internet of Things) Solutions:Cloud hosting providers offer IoT platforms and services for businesses looking to connect, manage, and analyze data from IoT devices. This is essential for industries like manufacturing, agriculture, and smart cities.
Security in Cloud Hosting

Cloud hosting providers implement a range of robust security measures to ensure the protection of your data and applications. Let’s delve into the key security considerations in cloud hosting:
1. Cloud Security Best Practices:
- Cloud hosting providers follow industry best practices to safeguard your data and applications. To secure data while it’s in transit and at rest, encryption must be used. With encryption, you may be sure that even in the event of illegal access, the data cannot be read without the right encryption keys.
- To limit who has access to and authority over cloud resources, access controls are implemented. To guarantee that only authorized users and apps can interact with your hosted assets, providers deploy robust authentication techniques and authorization regulations.
- Vulnerabilities and weaknesses are found during routine security audits and assessments. These evaluations support providers in continuing to take preventative measures against possible dangers and protect the security of their infrastructure.
2. Disaster Recovery and Backup:
- Cloud hosting providers offer comprehensive disaster recovery solutions. They replicate your data and applications across multiple data centers, often in different geographic locations. This redundancy ensures that even in the event of hardware failures or natural disasters, your data remains accessible.
- Backup services are typically automated, allowing you to schedule regular backups of your data. This redundancy offers peace of mind, knowing that you can recover your data in case of accidental deletions, data corruption, or other unexpected incidents.
3. Identity and Access Management (IAM):
- IAM solutions enable you to control and manage user and application access to your cloud resources. You can create roles, set permissions, and enforce policies to ensure that only authorized individuals or systems can make changes or access data.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is often implemented to add an extra layer of security. This requires users to provide additional verification, such as a code sent to their mobile device, in addition to their password.
4. DDoS Protection:
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can disrupt your online services by overwhelming your infrastructure with a flood of traffic. Cloud hosting providers often have DDoS protection measures in place to mitigate these attacks, ensuring your services remain accessible to legitimate users.
5. Compliance and Certifications:
- Cloud hosting providers adhere to industry-specific compliance standards and often hold certifications that attest to their security practices. This includes standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR compliance, which can be crucial for businesses with specific regulatory requirements.
6. Security Monitoring and Incident Response:
Providers implement continuous security monitoring to detect and respond to potential threats in real-time. They have dedicated security teams that respond to security incidents promptly and effectively.
Cloud Migration Strategies
Planning to migrate to the cloud? Follow these steps:
Planning and Execution:
- Assessment: Start by assessing your existing infrastructure, applications, and data. Identify what can be migrated to the cloud, as well as dependencies and any potential roadblocks.
- Goal Setting: Clearly define your migration objectives. Whether you aim to reduce costs, improve scalability, or enhance performance, your goals will guide your migration strategy.
Challenges and Solutions:
- Downtime and Business Continuity: Minimize downtime by using cloud disaster recovery and backup solutions. Implement failover mechanisms to ensure uninterrupted services.
- Security Concerns: Address security by leveraging the security features provided by your cloud hosting provider.
- Cost Management: Monitor and manage your costs closely. Use cloud cost management tools and implement cost control strategies like rightsizing resources.
- Compatibility Issues: Be prepared to adapt or refactor applications for cloud compatibility. This may involve changes to the code, database schema, or configuration settings.
Steps for Successful Cloud Migration:
- Create a Migration Team: Assemble a dedicated team with the necessary skills and expertise to manage the migration process effectively.
- Define a Migration Roadmap: Develop a detailed migration plan with a timeline, roles, and responsibilities clearly defined.
- Pilot Migration: Test the migration process with a smaller, non-critical workload to identify and address any issues before migrating critical data and applications.
Comparison with Traditional Hosting
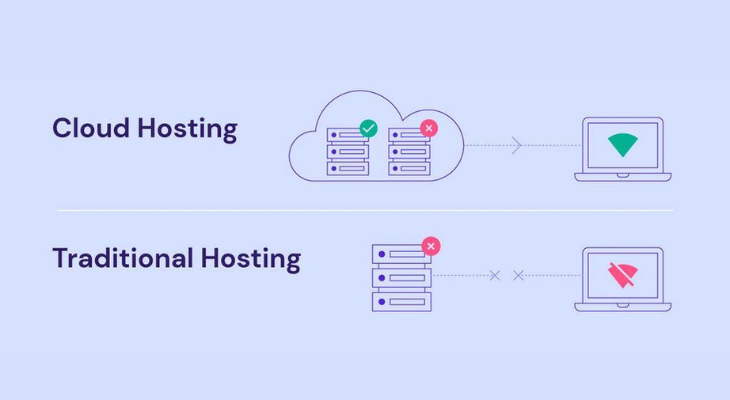
When it comes to hosting your digital infrastructure, you have two main options: cloud hosting and traditional hosting. Let’s compare these two approaches to help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs:
Cloud Hosting:
- Scalability:This scalability is ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads, ensuring that you only pay for what you use. In contrast, traditional hosting often requires manual hardware upgrades, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Reliability:Cloud hosting is designed with redundancy in mind. Your data and applications are stored across multiple servers and data centers, reducing the risk of downtime due to hardware failures or disasters. Traditional hosting may lack this level of redundancy.
- Cost-Effectiveness:Cloud hosting often follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where you’re billed only for the resources you use. This can be cost-effective for businesses with variable workloads. Traditional hosting may involve fixed costs, regardless of your usage.
- Disaster Recovery:Cloud hosting providers typically offer robust disaster recovery solutions, including automated backups and failover options. Traditional hosting may require you to manage your own disaster recovery, which can be complex and costly.
Traditional Hosting:
- Simplicity:Traditional hosting is often more straightforward to set up, making it suitable for small-scale, static websites or applications. Cloud hosting can be more complex due to its flexibility and scalability.
- Cost Predictability:With traditional hosting, you typically know your fixed monthly or annual costs. This cost predictability can be advantageous for budget planning. In contrast, cloud hosting costs can vary depending on your usage, which may require careful monitoring.
- Customization:Traditional hosting allows for more direct control over your hardware and software configuration. This level of customization can be valuable for businesses with specific requirements. Cloud hosting may limit some customizations due to its standardized infrastructure.
- Resource Constraints:Traditional hosting is subject to resource constraints, as you are limited by the physical hardware you have. Cloud hosting offers virtually limitless resources, making it more suitable for applications with dynamic workloads.
Conclusion
The cloud hosting journey can be transformative for your business. Embrace the future of IT and enjoy the benefits of flexibility, scalability, and security. If you have more questions or need further guidance, don’t hesitate to reach out to us or your chosen cloud hosting provider. Welcome to the cloud revolution!
FAQs about Cloud Hosting
Describe cloud hosting and explain its operation?
Cloud hosting is a service that allows you to host your websites, applications, and data on remote servers maintained by cloud service providers. It works by storing your data and applications in a distributed, virtualized environment. When a user accesses your content, the cloud server delivers it over the internet. The key benefit is scalability, which means you can easily adjust your resources as your needs change.
How do I choose the right cloud hosting provider?
Selecting the right cloud hosting provider depends on your specific needs, budget, and preferences. Consider factors such as the provider’s reputation, available services, pricing, security features, and customer support. Assess whether the provider’s offerings align with your business requirements and long-term goals.
What are the security measures in cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting providers employ a range of security measures, including encryption, access controls, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits. Data centers are often physically secured, and providers implement multiple layers of security to protect your data from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other threats.
What is the cost structure of cloud hosting?
The cost structure of cloud hosting typically includes a combination of factors, such as the resources you use (compute power, storage, bandwidth), the duration of usage, and any additional services you require. Some cloud providers offer pay-as-you-go pricing, where you pay only for what you use. Others may offer fixed pricing models. It’s essential to understand the provider’s pricing structure to estimate your costs accurately.
How does cloud hosting compare to traditional hosting?Cloud hosting differs from traditional hosting in several ways. Cloud hosting provides scalability, allowing you to easily adjust resources, while traditional hosting often requires manual hardware upgrades. Cloud hosting is typically more reliable due to redundancy, and it offers better disaster recovery options. However, traditional hosting may be more straightforward and cost-effective for small-scale, static websites.
How can I migrate my existing infrastructure to the cloud?
Migrating to the cloud involves several steps, including assessment, planning, migration, and post-migration testing. It’s crucial to evaluate your current infrastructure, choose the right cloud hosting provider, plan the migration strategy, and execute it systematically. You may choose to migrate applications, databases, or entire data centers. Working with cloud migration experts or utilizing migration tools provided by cloud providers can simplify the process and ensure a smooth transition.