Augmented Reality (AR): Future of AR

Augmented Reality (AR) has rapidly emerged as a transformative technology, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. Augmented Reality (AR) improves our vision and engagement with the world around us by superimposing computer-generated content over our actual surroundings. This article explores the intriguing field of augmented reality (AR), looking at its implications, applications, and providing answers to some commonly asked issues.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is augmented reality (AR)?

The real-time integration of digital information with the user’s surroundings is known as augmented reality, or AR. Users of augmented reality (AR) see the real world with created perceptual information superimposed on top of it, in contrast to virtual reality (VR), which generates an entirely fabricated environment.
Users can receive more information via augmented reality, or it can be utilized to visually alter natural landscapes. The main advantage of augmented reality (AR) is its ability to integrate digital and three-dimensional (3D) elements with a person’s reality experience. AR has several applications, ranging from entertainment to decision support.
The device overlays this data to produce an immersive experience that modifies the user’s perspective of the physical environment through digital information. Part of the natural world might be hidden or enhanced by the information that is superimposed over it.
Thomas Caudell, a researcher at Boeing Computer Services Research, first used the phrase “augmented reality” in 1990 to characterize the functionality of head-mounted displays used by electricians to put together intricate wiring harnesses. During some point in 1998, televised football games featured a yellow first down marker, which was among the first commercial uses of augmented reality technology.
Currently, the most well-known consumer augmented reality devices include Google Glass, smartphone games, and heads-up displays (HUDs) in automobile windshields. However, a wide range of businesses, including marketing, public safety, gas and oil, healthcare, and tourism, also use technology.
How does Augmented Reality work?
There are several ways to deliver augmented reality, such as through smartphones, tablets, and eyewear. Additionally, contact lens-delivered augmented reality is being explored. Hardware elements like a processor, sensors, display, and input devices are needed for the technology. This hardware is often already present in mobile devices, which feature solid-state compasses, cameras, accelerometers, and GPS systems.
This contributes to increasing AR’s usability for regular users. For example, a device’s compass can be used to determine device orientation and a GPS can be used to determine the user’s exact location.
Advanced augmented reality training programs employed by the military may encompass machine vision, object identification, and gesture recognition. Since augmented reality (AR) can be computationally demanding, data processing can be sent to a different processor if a device is underpowered.
Developers can link animation or contextual digital data in an app’s computer program to an augmented reality marker in the actual environment by writing augmented reality apps in specialized 3D programming languages. The AR app or browser plugin on a computing device starts to run the code of a known marker and layer the appropriate image or images when it gets digital information from the marker.
Examples of Augmented Reality

A few retail industry pioneers have created augmented reality (AR) technologies that aim to improve the shopping experience for customers. Store catalog applications have used augmented reality to let customers see what various products might look like in various settings. When purchasing furniture, for instance, customers can position the camera in the direction of the desired room, and the item will come into focus.
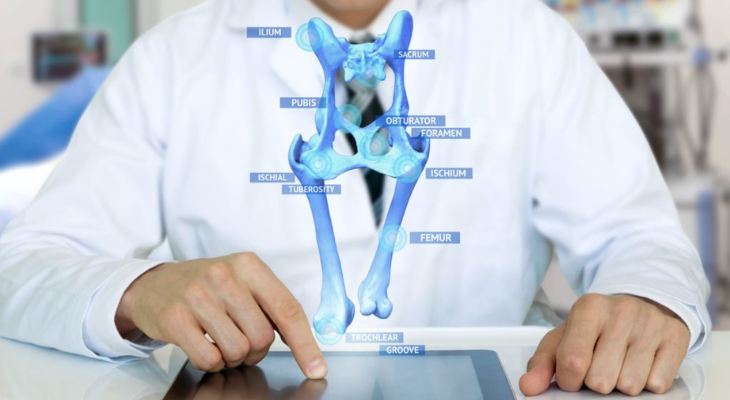
The benefits of augmented reality may also apply to the healthcare industry, where it may have a significant impact. When a mobile smartphone is held over a target image using augmented reality (AR) software, users can view incredibly detailed, three-dimensional views of various body systems. The application of AR in medical professional education has grown to be a potent learning tool.
Augmented Reality vs. Virtual Reality
Let’s be clear because augmented reality and virtual reality are sometimes misunderstood. In order to improve the experience, augmented reality overlays a virtual environment or virtual information on top of the real one. Consider the popular mobile game Pokémon Go, where players explore their actual neighborhoods in pursuit of animated figures that appear on their phones or tablets. AR technology is being used by NFL broadcasters to enhance their play analysis.
On the other hand, virtual reality transports people to a completely new setting, usually one that has been digitally designed and produced. Users of virtual reality, for instance, can find themselves submerged in an animated scene or an online world. Another way to use virtual reality is to take pictures of real-world locations and include them into VR applications. A virtual reality headgear allows one to explore Italy as if it were their own country.
What Is Augmented Reality Used for?
A natural environment can be visually altered via augmented reality, or it might be improved by adding new information. It can be applied to many different fields, including as industrial manufacturing, education, gaming, home and building design, marketing campaigns, and product visualization.
Advantages and Benefits of AR
- Enhanced User Experiences: By superimposing digital content over the actual environment, augmented reality (AR) offers consumers dynamic and captivating experiences. AR brings a new degree of engagement and immersion to games, entertainment, and education.
- Improved Learning and Training Outcomes: In education and training, AR can make complex concepts more understandable. With the help of the practical learning opportunities it provides, learners may visualize and engage with the material more naturally.
- Medical Advancements and Patient Care: AR is used in healthcare for medical training, surgery planning, and even during surgical procedures. It improves patient outcomes by assisting medical practitioners in comprehending and navigating complex medical data more effectively.
- Sales and Marketing Advantages: In the retail industry, AR is employed to provide customers with immersive product experiences. Before making a purchase, customers may see things in their own settings, which boosts sales and lowers the number of returns.
- Architectural Visualization and Design Benefits: Architects and designers use AR to create 3D models of their projects and overlay them onto real-world settings. Clients are better able to investigate and comprehend designs as a result, leading to improved decision-making and project outcomes.
- Industrial Efficiency and Safety Enhancements: In manufacturing and industrial settings, AR is used to assist workers in assembly, maintenance, and quality control. It offers visual advice in real-time, which lowers errors, boosts productivity, and increases safety.
- Enriched Tourism Experiences: AR apps and devices enhance tourism by providing tourists with historical and informational overlays. Travelers’ experiences can be enhanced by using augmented information to explore historical places and landmarks.
- Real-time Information and Data Access: AR enables users to access real-time information and data relevant to their surroundings. AR apps, for instance, can translate languages, provide context for artwork in museums, and provide information about nearby attractions.
- Remote Assistance and Collaboration: Augmented Reality (AR) enables professionals to offer advice via AR glasses or other devices, even when they are geographically apart. For technical assistance and field service operations, this is especially helpful.
- Increased Accessibility: AR has the potential to improve accessibility for individuals with disabilities. Augmented Reality (AR) has the potential to improve accessibility and inclusivity for individuals with diverse physical or sensory needs by offering real-time information and support.
Is Augmented Reality or Virtual Reality More Realistic?

Augmented reality, which combines computer-generated visual elements with a real-world environment, has the potential to be perceived as more realistic than virtual reality, which is entirely computer-generated. But because to technological advancements, even completely simulated surroundings can appear lifelike.
- Applications of AR: AR has been used in a multitude of industries and has a wide variety of applications.
- Gaming: By fusing virtual worlds with real-world settings, well-known augmented reality games like Pokémon GO and Ingress have captured the attention of millions of players.
- Education: By utilizing AR to build immersive and interactive learning environments, learning can become more interesting and educational.
- Healthcare: While people gain from educational AR apps for self-care, medical professionals employ AR for procedures, diagnosis, and medical training.
- Retail: By enabling shoppers to see things in their homes before making a purchase, augmented reality (AR) is used to improve the shopping experience.
- Architecture and Design: By using augmented reality (AR), architects and designers may exhibit and see 3D models of their projects in actual settings.
- Manufacturing: By giving employees real-time visual direction, augmented reality (AR) helps with assembly, maintenance, and quality control.
- Travel: By adding historical and informative overlays, augmented reality apps enhance visitors’ sightseeing experiences.
The Future of Augmented Reality in Education
We had a ton of textbooks, looseleaf papers, posters, and other printed things back in the day while we were in school. All educational resources will be digitized, interactive, and always available because of augmented reality. Since classes may be conducted in the style of games, this will greatly increase the number of individuals who have access to education and provide a better degree of student interaction.
Additionally, you may bid adieu to school excursions to the museum or art gallery because, with the help of augmented reality, these establishments will travel to you and be accessible at all times. These are only a few of the augmented reality’s potential applications in the classroom; it will undoubtedly transform learning.
The Future of Augmented Reality
With the advancement of technology, augmented reality (AR) has a bright future. With better visuals, quicker processing, and more lifelike digital overlays, augmented reality is about to become even more immersive. A greater selection of augmented reality hardware, such as more fashionable and comfy AR glasses, is anticipated, making the technology more approachable and practical for everyday use. AR will gain from improved real-time data streaming as the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G connectivity grow, becoming even more dynamic and engaging. Context-aware and intuitive experiences will be made possible by the use of AI and machine learning in AR.
In addition, augmented reality (AR) is probably going to spread into new fields and uses, such telemedicine, remote work, and enhanced sports experiences. To ensure responsible and meaningful integration, it will be imperative to address ethical and privacy concerns as augmented reality becomes more commonplace. The boundaries between the real and digital worlds will likely become more hazy in the future thanks to augmented reality, which will present exciting new possibilities for creativity and improved human experiences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, augmented reality has the power to completely change how we see and engage with the world. The uses of this technology will grow as it develops, integrating augmented reality into our everyday lives. AR’s influence is already felt in a variety of fields, including industry, healthcare, education, and entertainment. The applications are virtually endless. In order to achieve responsible and meaningful integration, it is imperative that we investigate its potential benefits while addressing ethical and privacy concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
How is Augmented Reality different from Virtual Reality?
While virtual reality submerges users in a fully simulated realm and obscures the outside world, augmented reality adds digital components to the real world.
What devices are commonly used for AR experiences?
AR headsets, smart glasses, tablets, and smartphones can all be used to enjoy AR experiences.
Are there privacy concerns associated with AR?
Indeed, there are privacy concerns, especially with regard to data gathering, security, and the possibility of intrusive spying via augmented reality gadgets.
What industries are benefiting the most from AR technology?
Among the sectors that AR is greatly helping are gaming, education, healthcare, retail, architecture, and manufacturing.
How is AR expected to evolve in the future?
It is anticipated that augmented reality (AR) would get increasingly lifelike, with better graphics and more seamless interaction with daily life. It’s also probably going to spread into other markets and uses.




One Comment