Cybersecurity: Protecting Your Digital World

The concept of “cybersecurity” is used a lot in the modern digital era. It’s likely that you’ve heard of it from tech-savvy friends, the news, or job descriptions, but what does it actually mean and why is it so crucial? Let’s investigate the realm of cybersecurity and how it affects our daily life.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Cybersecurity?

Cybersecurity Meaning: Firstly, let’s define the phrase “Cybersecurity.” Cybersecurity, to put it simply, is the protection of your online environment. It’s similar to locking your front door to keep intruders out, only it works online. We safeguard the enormous amounts of data we keep and exchange online, as well as our PCs and smartphones.
Cybersecurity is a broad field with various aspects. Imagine it like a huge fortress, where every piece is a barrier against all others. Network security, data security, and endpoint security are some of these components.
- Network Security is like the gatekeeper of the fortress. It consists of technologies that filter out harmful communications and illegal access, such as firewall systems and intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS).
- Data Security is the treasure inside the fortress. To guarantee that sensitive data stays private and secure, it entails utilizing encryption and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) techniques.
- Endpoint security is comparable to the wall-patroling guards. It uses technologies like Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and antivirus software to shield specific devices from online dangers.
Cyber Security Types
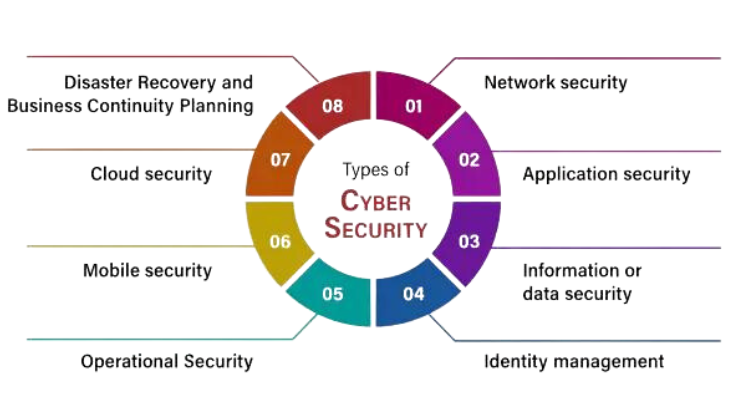
1. Network Security:
- Firewall Systems: Your network’s gatekeepers are firewalls. They keep an eye on all incoming and outgoing network traffic and use a set of security rules to determine which data packets to allow or prohibit.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): IDPS programs keep an eye on network traffic to look for unusual activity or patterns of known attacks. They have real-time intrusion detection and response capabilities.
2. Data Security:
- Data is transformed into a code through the process of encryption, which stops unwanted access. It guarantees that information is secure and confidential even in the event that it is intercepted.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP programs stop private information from being leaked or shared without authorization. Both inside and outside of a company, they keep an eye on and manage data exchanges.
3. Endpoint Security:
- Antivirus program: This program checks your device for viruses and malware that are known to exist. It aids in locating and eliminating dangers to maintain the integrity of your system.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions give businesses the ability to monitor and respond in real-time, enabling them to promptly identify and neutralize threats on individual devices.
- Cloud Security:
- Data stored in cloud services like Dropbox or Google Drive is protected by Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) solutions. They give visibility into cloud usage and enforce security regulations.
- Security as a Service (SECaaS): This concept is affordable and scalable for companies of all sizes, providing cybersecurity services over the cloud.
5. Application Security:
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): WAFs guard against cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection threats by screening and tracking HTTP requests.
- These tools are used to scan and test applications for vulnerabilities both during development and after deployment. They are called Static and Dynamic Application Security Testing (SAST and DAST).
6. IoT (Internet of Things) Security:
- Device authentication makes guarantee that only approved devices are able to connect to and interact with Internet of Things networks.
- Firmware Updates: In order to address security flaws, IoT device firmware must be updated on a regular basis.
7. Industrial Control System (ICS) Security:
- Security for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA): Guards against cyberattacks vital infrastructure systems, such as manufacturing facilities, water treatment plants, and power grids.
- Security for Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): Protects industrial process controllers.
8. Mobile Device Security:
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): MDM programs assist businesses in controlling and safeguarding staff mobile devices.
- Mobile App Security: Makes certain that security is taken into consideration while developing mobile apps in order to avoid data breaches.
9. Critical Infrastructure Security:
- Security of the energy sector is centered on protecting pipelines, power plants, and the electrical grid.
- Financial Sector Security: Guards against online attacks on banking and financial networks.
10. Social Engineering Protection:
- Phishing Awareness and Training: Assists people in identifying and avoiding phishing emails, which deceive recipients into divulging personal information.
- Social Engineering Testing: To determine how vulnerable an organization is to social engineering assaults, organizations test their systems.
The Importance of Cybersecurity
The significance of cybersecurity in the linked world of today cannot be emphasized. Our lives are becoming more and more digital, so it is critical that we safeguard our data, networks, and systems from online attacks. Cybersecurity is an essential component of personal safety and privacy for people and businesses of all sizes, not just governments and big enterprises.
- Protection of Sensitive Data:The safeguarding of private and sensitive information is one of the main justifications for the significance of cybersecurity. Intellectual property, financial records, personal information, and other types of data may be included in this data. This data may be compromised in the absence of sufficient cybersecurity safeguards, which could result in identity theft, financial fraud, and other grave repercussions.
- Prevention of Cyber Attacks:Cyberattacks can take many different forms, including as denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, phishing scams, malware, and ransomware. These assaults have the potential to impair business operations, result in losses, and harm an organization’s brand. Cybersecurity lessens the impact of these attacks when they do occur and aids in their prevention.
- Safeguarding Critical Infrastructure:Digital technology plays a major role in critical infrastructure, including transportation networks, water treatment facilities, and electricity grids. These systems could be the target of a devastating attack with far-reaching effects. Strong cybersecurity defenses are necessary to keep these vital systems safe from attackers.
- Protection of Privacy:Protecting personal privacy is important because of the growing amount of personal data that is kept online. Cybersecurity safeguards guard against unwanted access and data breaches, helping to ensure that confidential information stays that way.
- Business Continuity:Maintaining operations is essential for firms. By protecting data and systems against interruptions, cybersecurity contributes to the maintenance of business continuity. In the modern global digital economy, where downtime can cause significant financial losses, this is extremely crucial.
- Regulatory Compliance:Regulations requiring specific cybersecurity procedures to safeguard data and uphold customer trust apply to many businesses. There may be penalties and legal repercussions for noncompliance. Thus, keeping up strong cybersecurity procedures is crucial for adhering to regulations.
- Trust and Reputation:A cyberattack or data leak can undermine confidence and harm an organization’s brand. Partners, customers, and clients expect that their information will be handled securely and with care. Making a significant investment in cybersecurity shows accountability and reliability.
- National Security:Cybersecurity is not just for private companies. There is a risk to national security because state-sponsored actors may use cyberattacks to compromise vital infrastructure or pilfer confidential government data. Securing a nation’s interests requires robust cybersecurity measures.
- Economic Impact:Incidents involving cybersecurity can have a big financial impact. Companies may have to pay for legal fees, lost revenue, and recovery costs following attacks. Furthermore, fraud and identity theft can cause financial damages for individuals.
Cybersecurity Best Practices
Having covered the fundamentals, let’s talk about self-defense. Everyone needs to be aware of cybersecurity; it’s not only for techies. Following are a few best practices:
- User Training and Awareness: Stay informed about the latest threats and scams. Don’t download attachments from unidentified sources or click on dubious websites.
- Access Control and Identity Management: Use strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Patch management: Ensure that your equipment and software are up to date. Patches are frequently released by developers to address security flaws.
Emerging Cybersecurity Technologies
Threats change as technology does. Here are some emerging technologies in Cybersecurity:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: These technologies help in identifying patterns and anomalies in data, aiding in threat detection and prevention.
- Blockchain: Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain has potential in securing data and transactions.
- Quantum Computing’s Impact: Quantum computers may challenge existing encryption methods, leading to new security challenges.
Steps in Ensuring Cybersecurity
- Establish a Comprehensive Security Policy: Define rules and guidelines for your digital life. This covers incident response plans, data access controls, and password policies.
- Regular Vulnerability Assessments: Periodically scan your systems for vulnerabilities and address them promptly.
- Incident Response Planning: Develop a plan for what to do in case of a cyber-attack. By doing this, harm and healing time can be reduced.
Cyber Security Tips

1. Strong Passwords:
- For every internet account, create a different, complicated password.
- Make use of a mix of special characters, numerals, and capital and lowercase letters.
- Use a passphrase, which is a string of unrelated words that is simple to remember but difficult to figure out.
2. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
- Whenever possible, turn on 2FA, especially for your bank and email accounts.
- By requiring a second form of verification, such as a one-time code from an SMS or mobile app, 2FA offers an extra layer of protection.
3.Keep Software Updated:
- Update your software, web browsers, and operating system on a regular basis.
- Updates frequently contain fixes for security flaws that hackers could use.
4. Beware of Phishing:
- Unsolicited emails should be avoided, especially if they ask for personal information or have dubious links or attachments.
- Check the legitimacy of the sender before responding or clicking any links.
5. Use Antivirus Software:
- Install trustworthy antivirus software to find and get rid of viruses.
- Update the virus definitions and antivirus software regularly.
6. Secure Your Wi-Fi Network:
- Your WiFi router’s default password has to be changed.
- For your Wi-Fi network, use WPA3 encryption, and keep your Wi-Fi password private from unauthorized users.
7. Data Encryption:
- To prevent unwanted access, encrypt critical information on your devices.
- Utilize encryption software or turn on your operating system’s built-in encryption features.
8. Regular Backups:
- Make sure you frequently backup your critical files and data to the cloud or an external drive.
- Backups can be invaluable in the event that ransomware or other problems cause data loss.
9. Social Media Privacy:
- Examine and modify your social media privacy settings.
- Restrict the amount of information you disclose to the public and exercise caution when accepting friend or connection requests from people you don’t know.
Conclusion
To sum up, cybersecurity is an essential component of our digital life and not just a catchphrase. Gaining knowledge about its definition, elements, and recommended procedures will enable you to securely and confidently traverse the digital landscape. Thus, take the required precautions to safeguard your digital citadel and keep yourself updated about the always changing cyberthreat landscape. It’s important to protect your digital environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is cybersecurity important?
Cybersecurity is essential to protect sensitive information, prevent data breaches, maintain the privacy of individuals, and ensure the integrity of digital systems. Without it, cyber threats and attacks can cause significant harm.
What are common cybersecurity threats?
Common cybersecurity threats include malware (viruses, ransomware, spyware), phishing attacks, hacking, social engineering, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
What Are the Common Cybersecurity Myths?
Common myths include “I’m not a target” and “Antivirus software is enough.” In reality, everyone is a potential target, and multiple layers of security are essential.
How Can Individuals Protect Their Personal Data?
Protecting personal data involves using strong, unique passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and being cautious about the information you share online.
What Are the Current Trends in Cybersecurity?
Trends include increased use of AI and machine learning for threat detection, the growth of IoT security concerns, and evolving privacy regulations.




One Comment